At a time when “search engines” are striving to become “response generators” and the volume of indexed content has never been so important, what strategy is adopted?
The arrival of generative artificial intelligence now allows the creation of a volume of SEO content never before seen.
The creation of evergreen content, product sheets, blog articles, etc. of the correct level has never been so accessible thanks to tools and LLMs such as Claude from Anthropic for example.
Faced with this surge, you are forced to review your copy if you want to continue to make your brand exist in a new SEO model – dictated all the more by recent Google algorithm updates on the quality of content aka Google Hlepfull Happy.
Indeed, if the generation of content of a “correct” level is simplified, it is simplified for any user of Generative AI (your prospects, your customers, your competitors) but also for the search engines themselves like Google AI Overviews, Perplexity and more recently SearchGPT from OpenAI.
The old “search engines” are gradually becoming “response generators”.
And the advent of “meta search” will only accelerate this mechanism.
Search via social networks, C2C platforms (Leboncoin, Ebay, etc.) or marketplaces is exploding and each platform must offer new content, also generated largely by artificial intelligence.
The good news?
These different AI tools and AI-boosted search engines cannot put themselves in the Internet user’s place if they do not know how to query them correctly.
Thus, SEO strategies and associated content are very often the same: cold and without real added value (apart from the speed with which you generate them – which is already a revolution).
We are therefore observing a phenomenon of large-scale content duplication because a large part of what is produced by AI is a constant recycling of already existing information, whether by publishers (advertisers) AND by AI tools. (such as ChatGPT) or even search engines – Perplexity, SearchGPT, Google AI Overviews in the first place.
Indeed, on the side of search engines, the indexing of (your) content allows them to generate responses via generative Artificial Intelligence from them.
Publishers/advertisers also use (your) content indexed by LLMs (language model at the heart of different generative AIs) to regenerate new content. The snake therefore bites its tail infinitely…
And the marketers who understand this will be the first to succeed.
How to stand out from the crowd in SEO?
In SEO and Content Marketing, we have always had several unknowns in our equation:
- Which profiles are looking for information about a service or product in search engines?
- What are their intentions?
- Etc.
Since the beginning of SEO, this information has often been put aside because we historically had enough data to retrospectively analyze the profile of SEO audiences and then rectify the situation to optimize strategy and content.
At this stage, we therefore have:
- More content produced by new search engines, platforms and by users (early adopters) of LLMs
- Less data (GDPR, Cookies, etc.) a posteriori to study SEO audiences
How can generative AI help us solve this equation?
Let’s first look at the training methods and statistical capabilities of LLM (Large Language Model).
To generate responses as close as possible to human language, the LLMs were first trained on diverse and gigantic datasets.
As an example, here is the ChatGPT 3 training corpus (source OpenAI / Arxiv):
all content from Wikipedia (English training only): 3% of the training,
- content of web pages (your site among others), open discussion forums: 60% of the training
- posts from social networks like Reddit (English training only): represents 22% of the training,
- books, publications and scientific studies: represents 8% of the training,
- etc.
What does this training data tell us?
Generative AI tools have cast as wide a net as possible to train their models: content distributed by the different communities of experts and scientists, cold/hot content, literary styles, UGC (User Generated Content), etc.
The billions of statistical parameters of LLMs then allow them to detect both strong signals (high probability of the next token) and weak signals (low probability of the next token) on almost all issues: B2C, B2B, information, services or products.
And this is exactly what we are looking for when we want to create personas (be careful of the hallucinations generated!) for our content!
But certain data is missing in the training corpora… And only the search engines have it: the keywords actually entered by the personas.
This is also – beyond the potential for monetizing its audience – one of the reasons why ChatGPT had to develop SearchGPT (its search engine still in beta): to obtain data (first party moreover) on what we are looking for / how we are looking for it.
Because the keywords are the mirror of the buyers’ profiles: for the same final search (information, a product or a service), the keywords can diverge greatly depending on the ability to write a query or even on the profile of the buyer. Internet user (connoisseur vs novice).
And if you want to create truly “people-first” content to meet the challenges of Google Helpfull Content, you must integrate it into your approach.
This is how the concept of “Search Buyer Persona” created by CyberCité was born.
The primary goal is not to generate new keywords but to first understand what is hidden behind your top business keywords. Those which produce transactional effects.
Beyond the “buyer persona” known in marketing, the “search buyer persona” completes the analysis with this SEO approach.
At the macro level, LLMs assist you in defining your ideal targets then broken down into personas. Then, you “AI-augment” your personas using your “keyword” data.
An example to illustrate:
You are a general building company specializing in “renovation”, the target you want to work on in SEO and SEA: “owners of individual houses”.
The “classic persona” variation allows you to obtain, for example, pain points for this target, such as:
– high material costs
– uncertainty about the skills of craftsmen
– fear of going over budget
– difficulty choosing quality materials
– compliance with safety standards
– complexity of administrative procedures
If you coupled this analysis with the “Search Buyer Persona” approach, here’s what you could expect:
– optimize expenses
– complete the project on time
– maximize the added value of the work
– plan the investment
This is a complementary vision much closer to the intentions of the persona worked on.
And for all those who have already had to plan an editorial strategy for creation or optimization, the contribution of the Search Buyer Persona is a real game changer to differentiate themselves from competing content.
Your SEO / Content Marketing strategy becomes more “surgical” to reach Internet users – prospects or customers – because it allows you to read between the lines of keywords.
You can then imagine the content strategies that will make you stand out from the crowd by responding to Google’s algorithms.
In our example, this approach enlightened us on an intention that we had never addressed in our content (we had already worked on the other 3 in our editorial SEO strategy): how to maximize the value of a renovation? In other words: what renovation work brings the most value to your home?
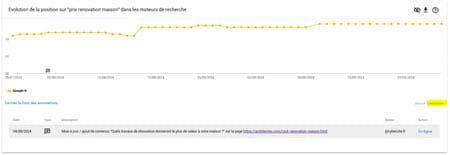
On 08/04/2024, we then put 1 content online to respond to this particular intention by wishing to reach 2 targets: owners of primary residences and real estate investors.
The content was indexed in a few days and here are the positioning results 6 weeks later: from 9th to 1st on one of our most transactional keywords in the client’s thesaurus:

In 2025, standing out from the crowd in SEO requires an AI-augmented approach that combines multi-intentional analysis, cross-referencing of data sources and finally human creativity.