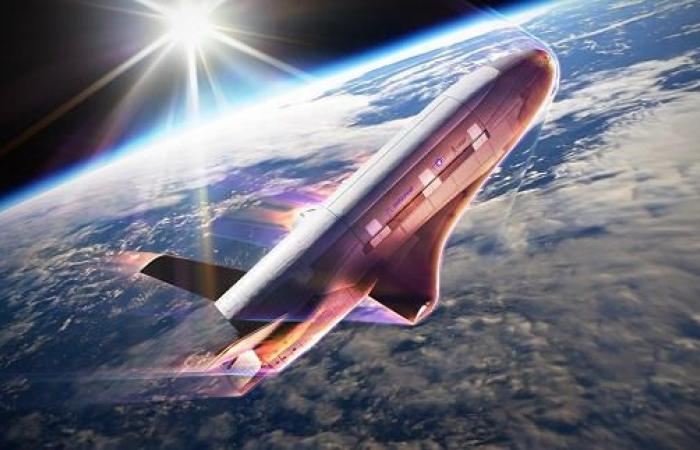
Put into orbit for the first time in 2010, the American military space drone X-37B, developed by the Phantom Works division, raises many questions, as the Pentagon remains discreet about its missions [qui sont toujours de plus en plus longues] and its capabilities.
One of the few things we know about it is that it has the ability to easily maneuver in orbit, and therefore to change altitude to escape from overly curious “foragers” or approach other satellites. It “frustrates our adversaries” and “we know it drives them crazy,” admitted Heather Wilson, then secretary of the US Air Force, at the Aspen Security Forum. [Colorado]in 2019.
Furthermore, we also know that it is equipped with a service module used to carry out experiments in orbit. Experiments whose nature has not always been specified by the Pentagon. Additionally, it can carry an additional payload attached to the rear of its fuselage.
Finally, the US Air Force indicated that it was considering “connecting” this X-37B to its F-22 and F-35 fighter jets in order to have the capacity “to operate in all domains”.
In any case, on December 28, a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket launched from Cape Canaveral [Floride] to put one of the two X-37Bs operated by the US Space Force [USSF] in a highly elliptical orbit. Which was a first. The Pentagon then explained that this seventh mission would consist of testing “new orbital regimes”, experimenting with “future technologies on knowledge of the space domain” and studying “the effects of radiation on materials provided by NASA [agence spatiale américaine, ndlr] ».
On October 10, while the details of this mission, designated OTV-7, were classified, the USSF nevertheless announced that the modify its orbit” and “safely dispose of components of its service module, in accordance with recognized space debris mitigation standards.”
As a reminder, aerobraking is a technique consisting of modifying the characteristics of the elliptical orbit of a spacecraft using the drag exerted by the Earth’s atmosphere. Which saves fuel [et / ou d’augmenter la charge utile]. This type of maneuver is part of the concept of “dynamic” space operations that American forces are seeking to develop.
“Once the aerobraking maneuvers are completed, the X-37B will resume its experiments until they are completed. At that time, it will deorbit and make a safe return as it did on its previous six missions,” the USSF explained.
“This series of innovative and effective maneuvers demonstrates the Space Force’s commitment to achieving groundbreaking innovations in the conduct of national security missions in space,” commented Frank Kendall, current Secretary of the US Air Force. .
As a reminder, powered by a Pratt&Whitney Rocketdyne engine, the X-37B measures 8.38 m long with a wingspan of 4.57 m and a height of 2.9 m. Its empty mass is around five tonnes.
Photo : Boeing