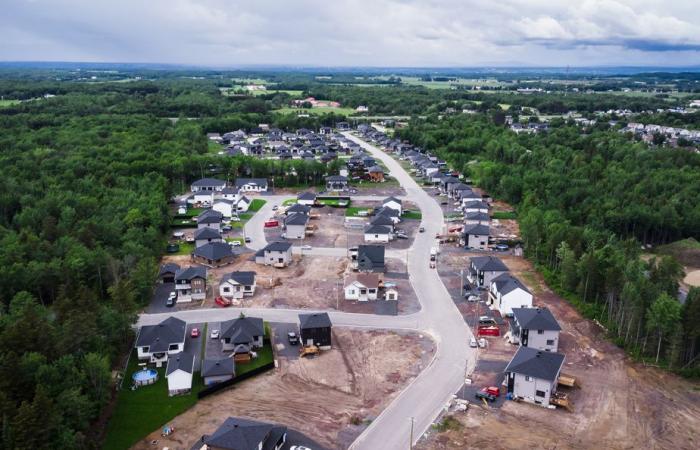
(Saint-Apollinaire) Jonathan Moreau grew up in a village. Today he is mayor of a city… and he hasn’t moved!
Posted at 5:00 a.m.
“In front of my house, when I was little, it was a field. We left by bike and returned at dusk. Now, in front of my parents, it’s a residential area,” says the mayor of Saint-Apollinaire.
The municipality of some 9,000 inhabitants is growing faster than its shadow. Its population increased by 30.4% in five years, between the 2016 and 2021 censuses. It is the city of more than 5,000 inhabitants with the strongest growth in Quebec, the fourth in Canada.
Saint-Apollinaire owes its growth in large part to its location. The city is attached to Highway 20, less than 30 minutes – when there is no congestion – from Lévis and the Pierre-Laporte bridge, which leads to Quebec.
Saint-Apollinaire is not an anomaly. The four other Canadian cities that grew the most between the last two censuses are suburbs on the outskirts of Toronto, Victoria and Winnipeg.
The recent work of a Canadian researcher leaves no doubt: the suburbs largely dominate the country, and they are constantly gaining ground.
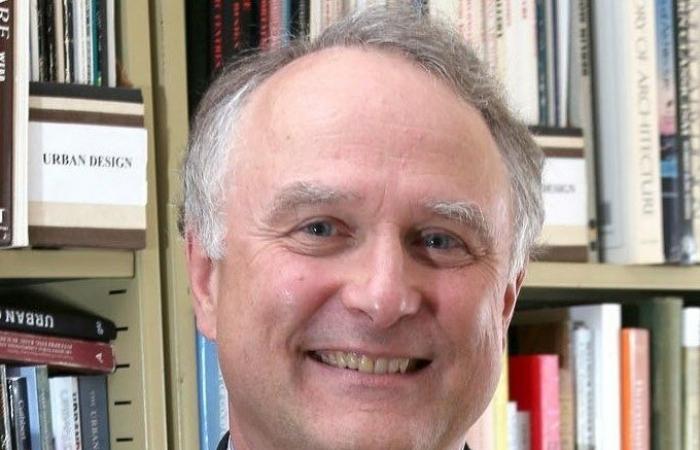
PHOTO FROM QUEEN’S UNIVERSITY WEBSITE
David Gordon, professor of urban planning at Queen’s University
Canada is a suburban nation. Suburbs are growing faster than cities, despite all our urban planning policies.
David Gordon, Professor of Urban Planning, Queen’s University
A trend that is confirmed
This professor of urban planning at Queen’s University became obsessed with the suburbs a few years ago. In an interview, he said that he had been consulted as an expert by the federal government. Ottawa wanted to set up an infrastructure fund for public transportation.
“A senior official said: “The census has just told us that Canada is 82% urban, so we need metros, metros, metros…”
David Gordon was startled. It was not subways that were needed, but light trains, because it was obvious, in his eyes, that growth was taking place in the suburbs.
The senior official did not budge. He even asked Professor Gordon for figures on the Canadian population living in the suburbs. But these figures did not exist.
The pugnacious academic set out, with his team, to answer this question. It wasn’t easy. It took five years.
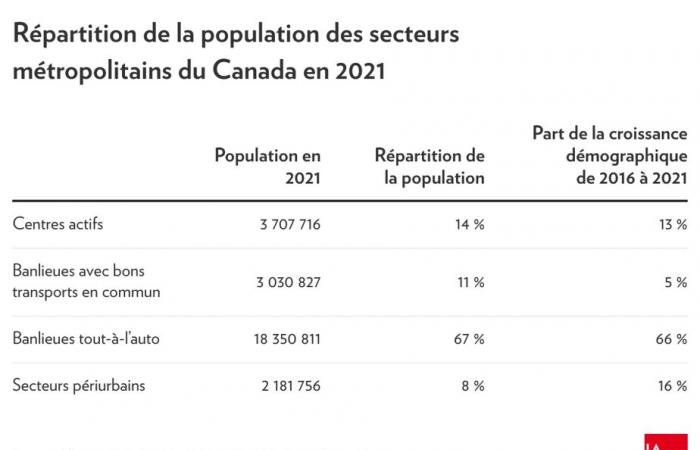
He had to comb through all 41 census metropolitan areas. By studying the maps one by one, he and his team divided metropolitan areas into four zones: “active centers,” where there are several transportation options other than the car; suburbs with well-developed public transport, such as certain districts of Longueuil; the suburbs where the automobile dominates; and peri-urban areas, almost rural places where more than half of workers commute to the city.
Do you live in the city or in the suburbs? Consult the map of Professor Gordon and his team (in English)
His conclusion? “Canada is two-thirds suburban,” says Mr. Gordon. The latest update of its study, published recently, indicates precisely that 66% of Canadians live in the suburbs.

This phenomenon is not running out of steam. Between 2016 and 2021, 66% of the population increase in metropolitan regions took place in car-dependent suburbs, and 16% in peri-urban areas, even further away.
Across the country, the latest census figures run through the professor’s analysis tool show that 82% of the Canadian population lives in a car-dominated area, with few or no public transportation options. .
The ideal of the bungalow
Why care about urban sprawl? Experts agree that this phenomenon has significant repercussions on society.

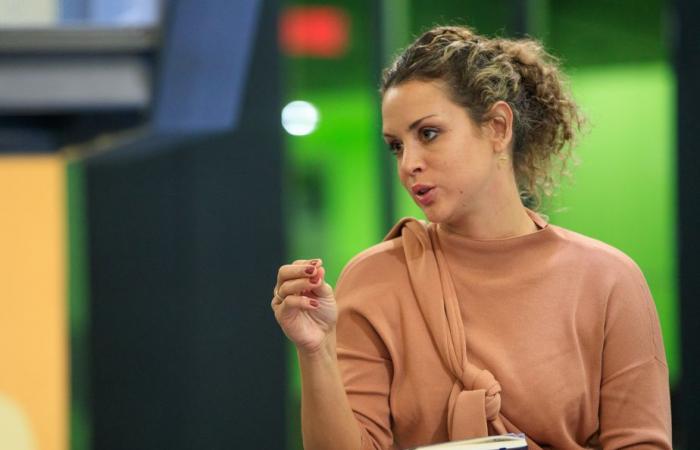
PHOTO HUGO-SÉBASTIEN AUBERT, LA PRESSE ARCHIVES
Fanny Tremblay-Racicot, doctor in urban planning and associate professor at the National School of Public Administration (ENAP)
“It’s important for environmental reasons. If we live more in the suburbs, it is certain that we will drive more, emit more CO2, use more space. So, it has an impact on congestion, on agricultural land, social development too, the quality of life, the social fabric…”, lists Fanny Tremblay-Racicot, doctor in urban planning and associate professor at the National School of public administration (ENAP).
“It also has an impact for public authorities. It’s more expensive in infrastructure, more intensive in public infrastructure,” she says.
David Gordon also sees an issue with the aging of the population.
There is a question of social equity. If you are too poor, too young or too old, the suburbs don’t work for you, because you can’t drive a car.
David Gordon, Professor of Urban Planning, Queen’s University
It is clear that, despite government policies with exotic acronyms, although very Quebecois, such as PNAAT or OGAT*, urban sprawl continues.
“For many people,American way of life with the automobile and the ownership of a single-family home remains a very strong ideal, notes Gérard Beaudet, professor of urban planning at the University of Montreal. We know that for 90% of families with young children, the ideal is a bungalow. It remains a very powerful ideal. »
-
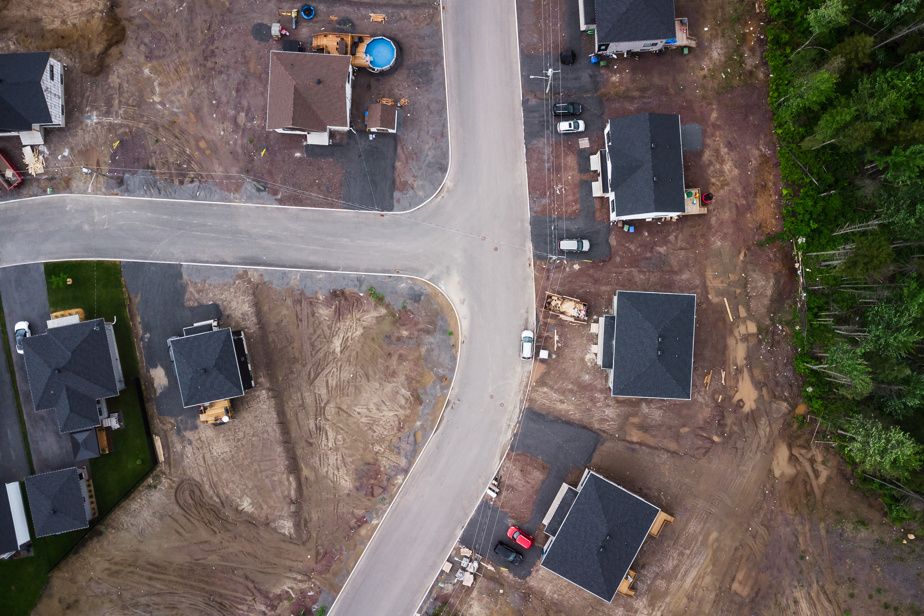

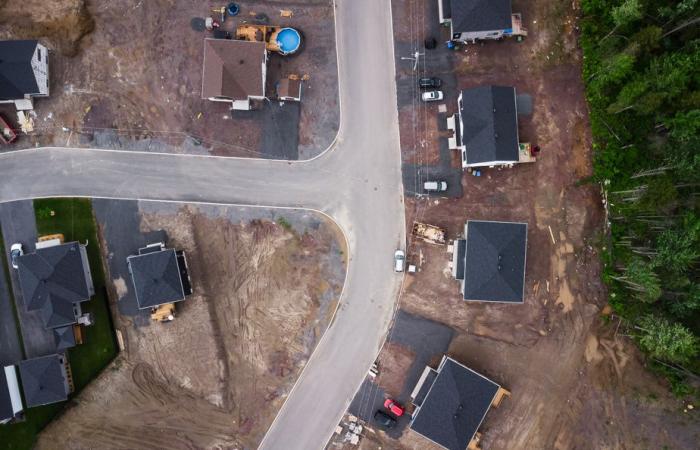
PHOTO EDOUARD PLANTE-FRÉCHETTE, LA PRESS
The municipality, which today has 9,000 inhabitants, could ultimately accommodate 13,000, according to town hall projections.
-
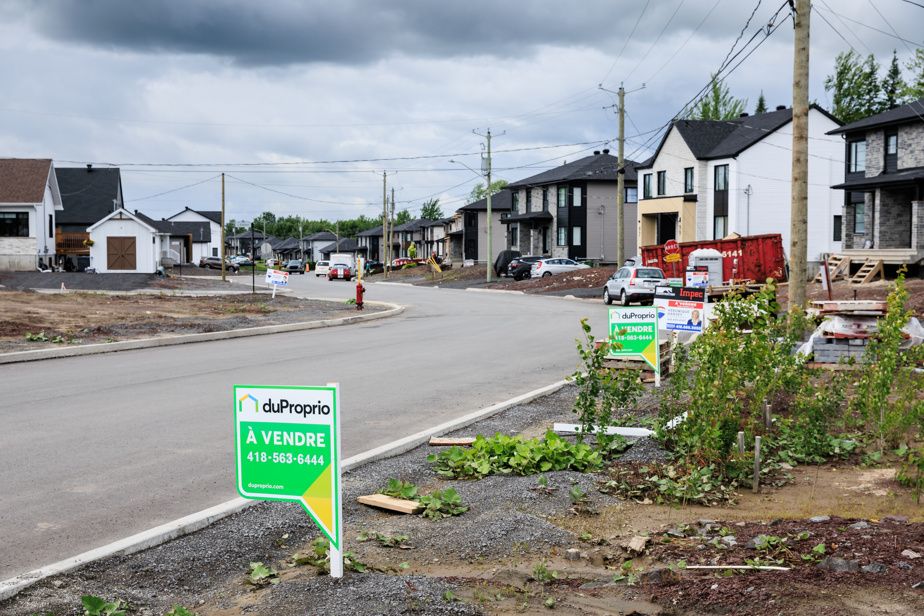

PHOTO EDOUARD PLANTE-FRÉCHETTE, LA PRESS
The relatively low price of houses compared to larger cities like Lévis particularly attracts young families to Saint-Apollinaire.
1/2
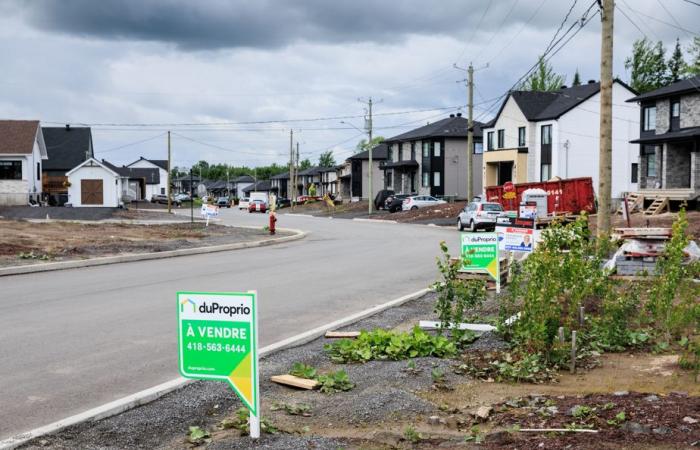
There are dozens of new houses growing in Saint-Apollinaire. As we pass by, rue du Geai-Bleu, workers are busy. An entire neighborhood is being born.
A quick search reveals a brand new semi-detached apartment for sale on the internet, with five bedrooms, for $298,000. A godsend in these times. The price of houses in the city is out of reach for the majority of families.
“We will not hide it, the further away you go, the more affordable the land is. So there are a lot of young families looking for a first home,” notes Jonathan Moreau.
The mayor expects, during the 2026 census, growth similar to that of recent years. Ultimately, he thinks that Saint-Apollinaire can accommodate 13,000 people within its urban perimeter, or 4,000 more than today.
“We remain in our white zone. We thought about asking for an expansion of our urban perimeter. We know that the rules have tightened. But the municipality is sensitive to that, not to spread itself out for nothing,” says the mayor.
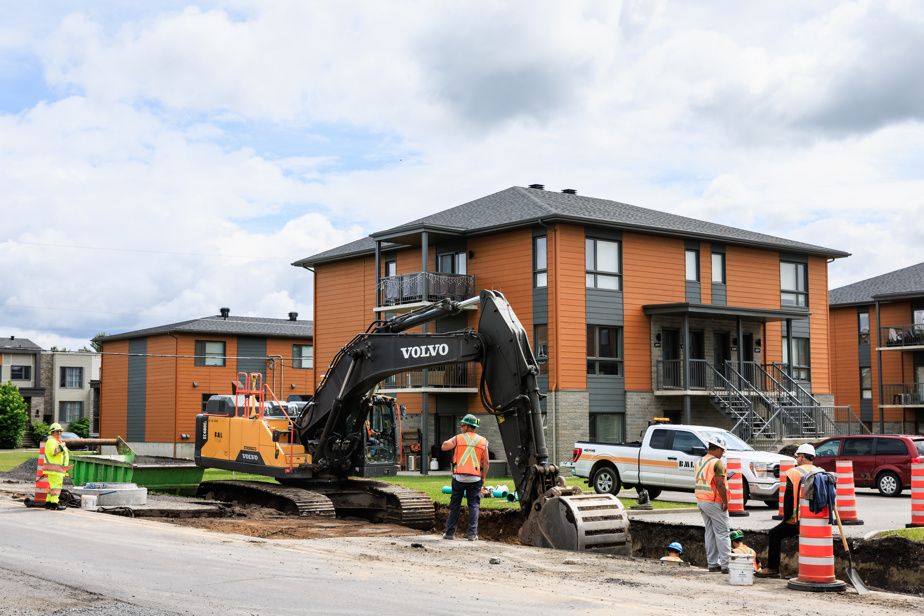

PHOTO EDOUARD PLANTE-FRÉCHETTE, LA PRESS
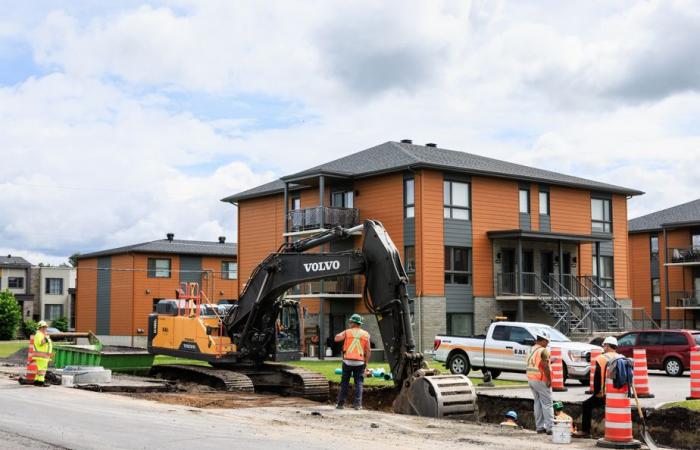
The municipality is banking in particular on multiplexes to become denser.
“So, we’re doing densification! “, he said. A dozen buildings of 20 units are under construction in the municipality.
But the fact remains that residents here are dependent on cars to get to town. Public transportation options are slim. The mayor would like to connect to the Lévis network. Meanwhile, congestion can be difficult during peak hours.
What does Mayor Jonathan Moreau think of the debates on urban sprawl? He understands the experts’ concerns, but he makes the argument of individual freedom.
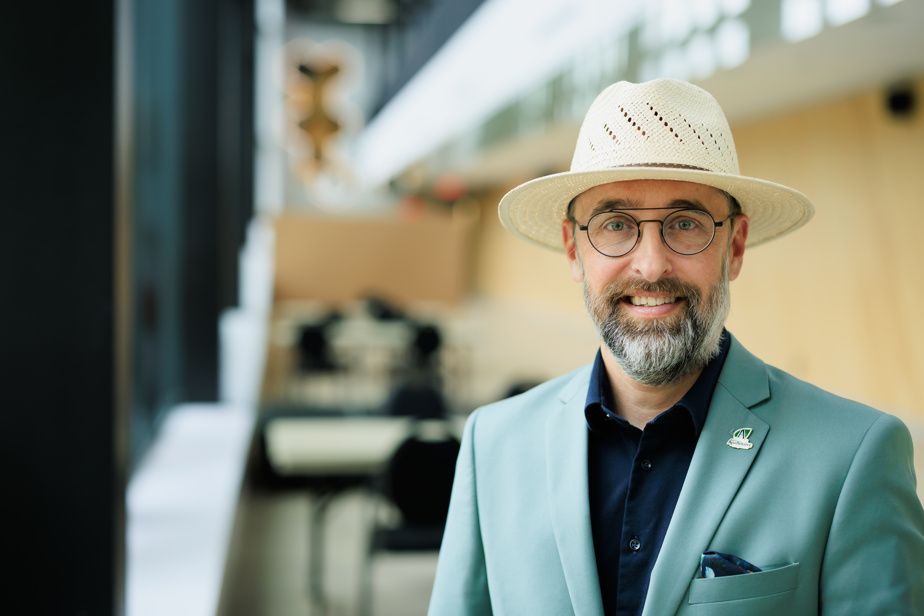

PHOTO EDOUARD PLANTE-FRÉCHETTE, LA PRESS
Jonathan Moreau, mayor of Saint-Apollinaire
You can’t stop us from existing. The municipality has existed for over 150 years. We cannot tell people: “Don’t come here anymore, everyone go to Quebec.”
Jonathan Moreau, mayor of Saint-Apollinaire
“I think that each municipality has a duty to densify and avoid sprawl,” believes Mr. Moreau. But it’s difficult to start saying: “You’re going to stay there and you’re going to stay there!” At that point, it’s communism, as far as I’m concerned. People have the freedom to choose, but the impact on the environment must be minimized. That, I agree. »
Professor David Gordon is sympathetic to the argument for individual freedom. “I worry because my research is often used by the libertarian right to say: ‘See, everyone loves the suburbs, we should just build more of them, stop worrying about this urban planning stuff.’ »
But according to him, this argument is incomplete. The exponential growth of suburbs doesn’t just reflect consumer preference, he says. “It also results from a choice by the government. There are plenty of subsidies and developments that make it easier to use the car and make public transport more difficult. It was thought to be the right thing to do after World War II. We didn’t know it didn’t work.
“As urban planners, we must recognize that this is desired by the majority of the population, but find better options. »
* National architecture and land use planning policy (PNAAT) and government guidelines for land use planning (OGAT)
What do you think ? Participate in the dialogue