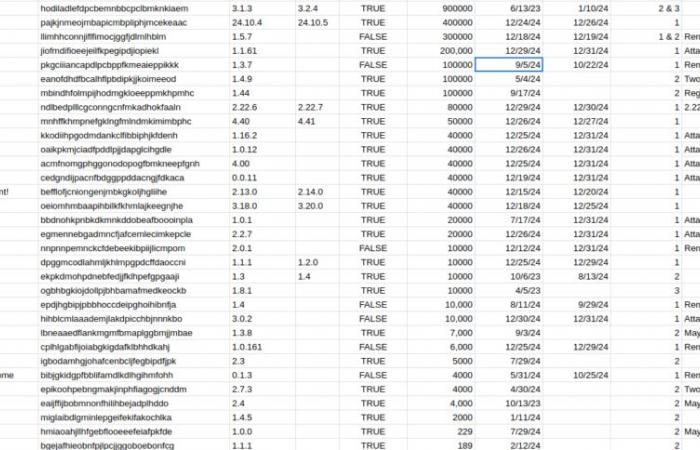
A new cyber malware campaign has targeted Chrome browser extensions. At least 35 add-ons are affected and represent a danger for Internet users.
Hackers never lack imagination when it comes to infecting a machine. While, in recent times, many viruses and other malware have targeted Android, a new campaign has just been discovered and this time concerns Chrome browser extensions.
More than thirty legitimate add-ons have been infected with malicious code and today represent a serious danger for the privacy and personal data of Internet users who use them, notes The Hacker News.
The list of affected extensions
Some extensions exfiltrate data to unsavory servers while others attempt to steal Facebook credentials to impersonate victims. The most vicious ones even go so far as to bypass two-factor authentication.
Some of its extensions have hundreds of thousands of installations, such as “ Reader Mode », « Visual Effects for Google Meet» or even «Bard AI Chat“. The full list of corrupted add-ons is visible on a public list established byThe Hacker News. And if several have been republished or cleaned of their malicious code, it is still advisable to get rid of them as quickly as possible.
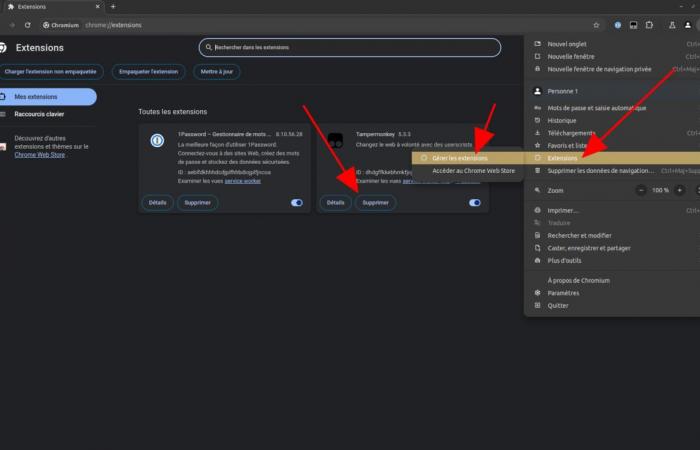
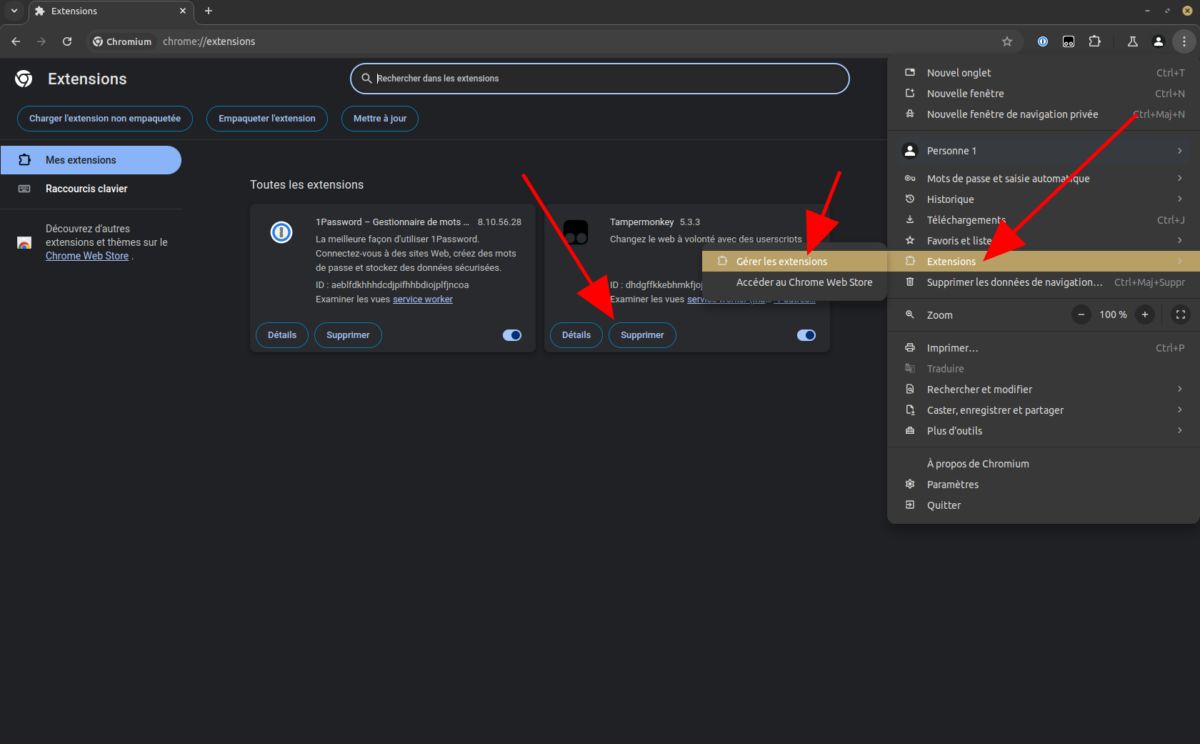
To uninstall a Chrome extension, nothing too complicated. Click on the three vertical dots in the browser window, go to the “Extensions“, Then “Manage extensions“. From there, remove any extensions affected by this hack and, while you're at it, uninstall any you don't use as well.
Indeed, browser extensions, like software, can sometimes have access to a lot of personal information. By limiting the number of extensions you use, you also limit the risk of unpleasant surprises.
A vicious infection method
The most surprising thing about this great campaign to corrupt Chrome extensions is undoubtedly the way in which the hackers operated. Rather than publishing malicious add-ons themselves, they infested the machines of “responsible” companies via a phishing campaign and then injected the malicious code into legitimate extensions.
To go further
The best extensions for Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge and Opera
Thus, hackers were able to gain access to an extremely large base of installed extensions with relatively little effort. Further proof that you have to be very careful about what you install on a machine, even when the name of the software inspires confidence.