Each of the 12 months of the yearthe moon reaches its maximum phase, the full moon, lighting up the night sky in an event that has captivated humanity for millennia.
Ancient civilizations, such as the Mayans, developed a sophisticated system of tracking the moon, while Native American people assigned unique names to each full moon, names that we still use today and which evoke traditions and activities from ancient times.
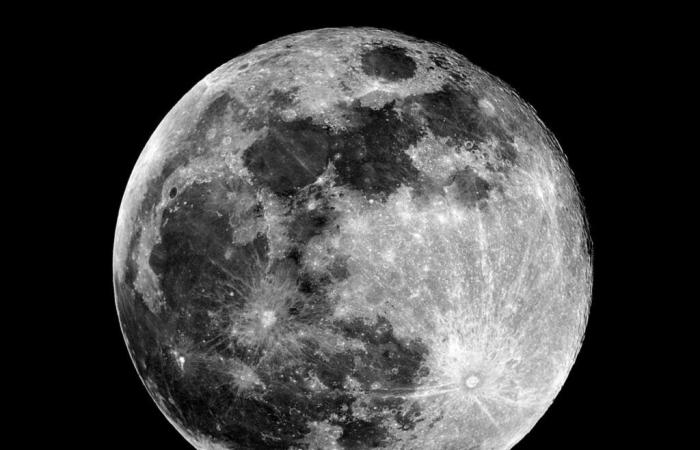
This month of November brings us the “Beaver Moon” but, unlike other years, that of 2024 will be very exceptional. This will be the fourth and final consecutive supermoon of the year, thus closing a very particular astronomical cycle which will not happen again until next year.
What is a supermoon?
According to NASA, A supermoon occurs when the full moon is at its closest point to Earth, making it appear larger and brighter than usual. The moon’s orbit around our planet is elliptical, not circular, so its distance from Earth varies.
When it is closest, the Moon is said to be at perigee, and when it is furthest away, it is said to be at its peak.
Although the extra size of a supermoon is not always noticeable to the naked eye, its brightness increases noticeably: according to Harvard University, a supermoon can be up to 30% brighter than a full moon traditional.
The supermoon phenomenon repeated several times in 2024, starting in August and reaching its closest point to Earth in October, when the distance was reduced to 357,364 kilometers.
When will the Beaver supermoon take place in November?
The impressive November supermoon, or full Beaver moon, will take place this Friday, November 15, 2024 and will reach its peak at 10:29 p.m. when it is in the constellation Aries. Although the exact time of the phenomenon is at this time, this phase of the Moon will be visible in almost its full magnitude from November 14 to 16. During these days, it will be 6.5% larger and 12.5% brighter than a regular full moon.
On this occasion, the Castor supermoon will be the most distant in a series of four consecutive supermoons, located 361,867 kilometers from our planet, according to NASA data. This circumstance is very timely, because the splendid moonlight will occur shortly before the maximum peak of the Leonid shower of shooting stars, visible every year between November 6 and 30.
To complete the astronomical month, on November 20, the Moon will pass close to Mars in the constellation Cancer, offering a visual spectacle in which the Red Planet will appear as a bright star very close to our natural satellite.
Why is it called the Beaver Moon?
The “Beaver Moon” takes its name from the ancient belief that it is during this month that the beavers create their lodges before winter and the rivers freeze. Additionally, from the 16th to the 19th centuries, November was the time when beavers grew their thickest fur, ideal for the fur trade, according to The Old Farmer’s Almanac.
To other cultures, this full moon is known as the “Frost Moon”, because it marks the start of the first frosts in the northern hemisphere, an important climatic event for agricultural practices and a reminder of the arrival of cold weather. This name is associated with the nature observation traditions of ancient societies, which organized their activities according to the rhythm of nature and the cycles of the Moon.