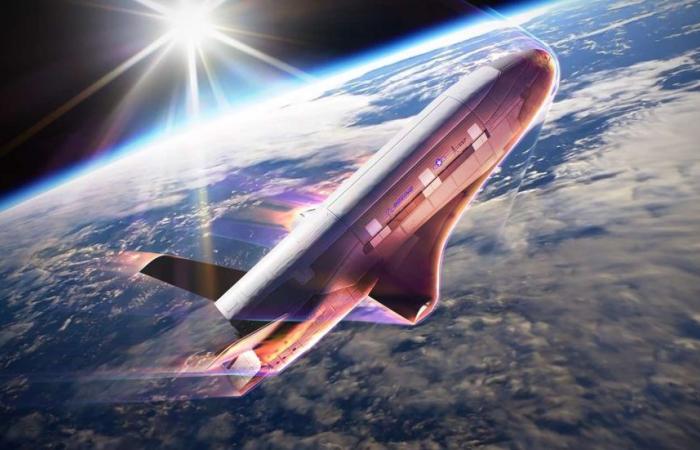
More than a month after the return to Earth of the Chinese space plane, which carried out a classified mission of 268 days, its American equivalent, the X-37B, operated by the United States Space Force (US Space Force))continues its own secret mission, started at the end of December 2023. The Pentagon then explained that this seventh mission aims to operate in “ new orbital regimes ”, to test and demonstrate “ technologies of the future » and also study the “ effects of radiation on materials, equipment and organisms ».
In a rare statement regarding this mission, the United States Space Force announced that the X-37B is preparing to conduct a “ series of new maneuvers, called aerobraking “. This technique aims to “ change its orbit » and “ safely remove components from its service module in accordance with recognized space debris mitigation standards ».
What is aerobraking?
Aerobraking consists of modifying the characteristics of a spacecraft’s orbit thanks to the drag exerted by theatmosphereatmosphere terrestrial. This technique saves fuel and is part of the “dynamic” space operations that American forces are seeking to develop. That is to say, improving its flight envelope by offering it interesting maneuverability capabilities useful for different activities such as advanced surveillance or escaping the surveillance of foreign satellites.
Although the principle seems simple, its applicationapplication practice is complex. Aerobraking maneuvers are not trivial and impose strong constraints on the vehicle, requiring rigorous control of its flight profile. One of the main challenges is not to go too low in the atmosphere, because the forces of frictionfriction can damage machine structures such as wings and control surfaces. In addition, this friction leads to a rise in temperature, which must be controlled to avoid damage to the structure. Conversely, if the vehicle merely skims the atmosphere, braking may be insufficient to change the orbital parameters. Calculating the optimal altitude requires a good knowledge of atmospheric density.
Space Rider, Europe’s future unmanned space plane
Perspective de missions
« Once the aerobraking maneuvers are completed, the X-37B will continue its experiments until their completion. At that point, it will deorbit and return safely, as it did on its previous six missions.s,” said the US Space Force.
Mastery of this technique offers numerous operational advantages. It not only allows substantial fuel reductions, but also flexibility orbitalorbital increased, making the vehicle more difficult to detect by opposing surveillance systems. It also expands the range of possible intelligence and testing missions.
Finally, the ability to control aerobraking is crucial if necessary, allowing a vehicle whose propulsion system is damaged, or not functioning properly, to return safely to Earth. This increases the X-37B’s ability to conduct covert or sensitive missions, enhancing its strategic value to the United States Space Force.
Two X-37Bs are said to be in service. Between them, they have carried out a total of six missions and a seventh is underway:
- OTV-1, from April 22 to December 3, 2010 (224 days);
- OTV-2, from March 5, 2011 to June 16, 2012 (469 days);
- OTV-3, from December 11, 2012 to October 17, 2014 (674 days);
- OTV-4, from May 20, 2015 to May 7, 2017 (718 days);
- OTV-5, from September 7, 2017 to October 27, 2019 (780 days);
- OTV-6, from May 17, 2020 to November 12, 2022 (908 Days).
- OTV-7 from December 28, 2023 to…