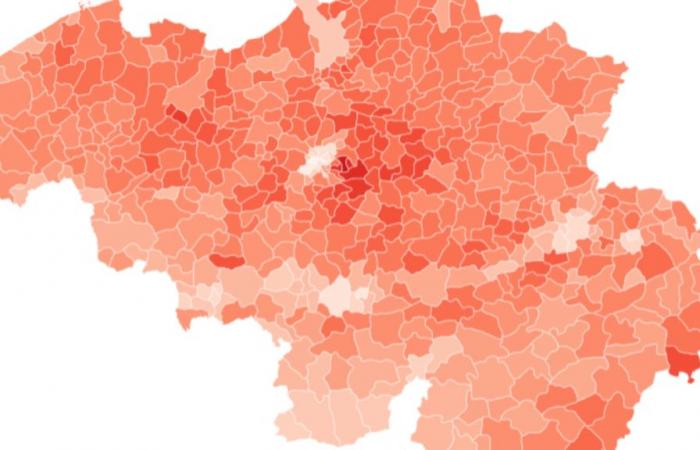
En 2022, Attert, in the province of Luxembourg, was the richest municipality in Belgium with a median net income of 42,211 euros, according to data from the Belgian statistical office Statbel. Saint-Josse-ten-Noode, in Brussels, had the lowest median income, at 19,288 euros. The two localities already occupied these same positions in 2020 and 2021.
Among the ten richest municipalities, six are located in the province of Luxembourg, namely Attert (42,211 euros), Messancy (37,226 euros), Etalle (34,978 euros), Saint-Léger (34,924 euros), Arlon (34,822 euros) and Habay (34,120 euros). Three municipalities are located in Flemish Brabant: Kraainem (36,531 euros), Tervuren (34,814 euros) and Wezembeek-Oppem (34,702 euros). Finally, Woluwe-Saint-Pierre (34,690 euros), in the Brussels Region, completes the ranking.
In contrast, six of the ten municipalities with the lowest incomes are located in the Brussels Region: Saint-Josse-ten-Noode (19,288 euros), Molenbeek-Saint-Jean (19,739 euros), Anderlecht (20,512 euros), Koekelberg ( 21,141 euros), Schaerbeek (21,726 euros) and Brussels city (21,862 euros). Two municipalities are located in Wallonia, more precisely in Hainaut: Farciennes (21,279 euros) and Charleroi (21,610 euros).
The income mentioned in this text is the administrative equivalent disposable income. This income, calculated using administrative data, takes into account, for the entire population, taxable and non-taxable (net) income (professional income, social benefits, pensions, integration income, rental income, income capital, family allowances, alimony, etc.). They are added together for all members of the household in order to obtain administrative disposable income for the household. After adjustment according to the composition of the household, we obtain the variable “administrative equivalent disposable income”. It can be used to calculate income and the risk of poverty at the municipal level. For more information, here is an article on the methodology used by Statbel.
Higher risk of poverty in Brussels
In terms of the risk of poverty, the lowest rates are recorded exclusively in Flanders, with Holsbeek and Zemst in the lead (3.4% each), followed closely by Boutersem (3.6%), La Pinte (3. 7%) and Herne (3.8%). Conversely, it is in the Brussels Region that the risk of poverty is most present: Saint-Josse-ten-Noode (34%) is ahead of Molenbeek-Saint-Jean (31.5%), Anderlecht (28.2%). %), Schaerbeek (26.8%) and Koekelberg (26.7%).
Figures on the risk of poverty at national and provincial level are published on the basis of the SILC survey, conducted by Statbel. Administrative Equivalent Disposable Income was developed on an administrative basis to match the household and income concepts of SILC as closely as possible and uses the same definitions. This makes it possible to map the risk of monetary poverty at the municipal level, but these figures in no way replace the national, regional and provincial poverty figures that Statbel publishes on the basis of data from the SILC survey, which meet a European standard allowing statistics to be compared within the EU.
Also read
Here is the average wealth of Belgians
Belgium





