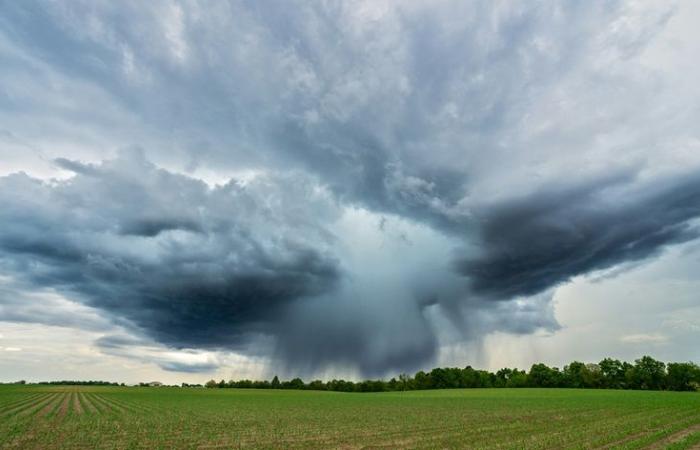
In 2024, and for the third consecutive year, more than 300 extreme weather events will affect the peninsula. In total, 351 storms, floods, droughts, hailstorms, tornadoes and record temperatures damaged Italy, six times more than the 60 episodes in 2015.
A number that has continued to grow over the last ten years: in 2024, there will be almost six times more extreme events than in 2015 (60), an increase of 485%.
According to the report published by the Observatory of the environmental association Legambiante, Emile-Romagna was once again the most affected region, followed by Lombardy, Sicily, Veneto and Piedmont.
“The fragility of our territory is due to two factors. The first is the strong anthropization, that is to say the transformation by man, which has led to the waterproofing of the soil. The second is industrial and agricultural development, which has taken away space from rivers”explains Davide Ferraresi, regional president of Emilia-Romagna of Legambiente.
Prolonged drought and increasing floods
Between too little and too much water, Italy is divided in two. The increase in damage linked to prolonged droughts (+54.5% compared to 2023), river floods (+24%) and floods due to heavy precipitation (+12%) weighed heavily in this estimate for 2024.
The year 2024 was marked by 134 cases of flooding due to heavy rains, 62 cases of wind damage, 46 river floods causing damage, 34 events with damage due to prolonged droughts, 30 cases of damage caused by hailstorms, 19 cases of landslides caused by heavy rains, 9 cases of infrastructure damage, 8 cases of damage caused by storm surges, 2 cases of damage to historical heritage, and 1 case of record temperatures.
Northern Italy hit hardest by the climate crisis
Northern Italy is hardest hit with 198 extreme weather events, followed by the south (92) and center (61). At the regional level, Emilia-Romagna, with 52 events, results as the region most affected by the climate crisis this year, followed by Lombardy (49), Sicily (43), Veneto (41) and from Piedmont (22).
Among large cities, Rome is the most affected with 8 extreme weather events, followed by Genoa (7) and Milan (6).
Sicily is the region most affected by drought in Italy (16 events), while Lombardy is the region most affected by floods (25 phenomena). Regarding river floods, Emilia-Romagna takes first place (with 14 events), followed by Lombardy (8) and Veneto (5).
Transportation damage
These extreme weather events have had an increasing impact on transportation in urban areas. Interruptions and suspensions caused not only by heavy rains, floods and landslides due to heavy precipitation, but also by record temperatures and strong gusts of wind. The most recent cases include the October 24 episodes in Rome, where a metro A station was closed due to flooding from heavy rain. A few days earlier, rail traffic was suspended on the Rimini-Ravenna line, due to severe weather. On September 5, a new flood of the Seveso river in Milan caused delays of more than two hours, compromised the circulation of certain tram lines and led to the closure of part of the M2 line.
2024, the year of records
A new global temperature record recorded by the European Copernicus program, which lists 2024 as the hottest year since records began with, for the first time, exceeding the threshold of 1.5 degrees compared to the era pre-industrial. November 2024 was the second hottest month globally, after November 2023, with an average air temperature of 14.1 degrees, +0.7 degrees compared to the average for this month between 1991 and 2020 .