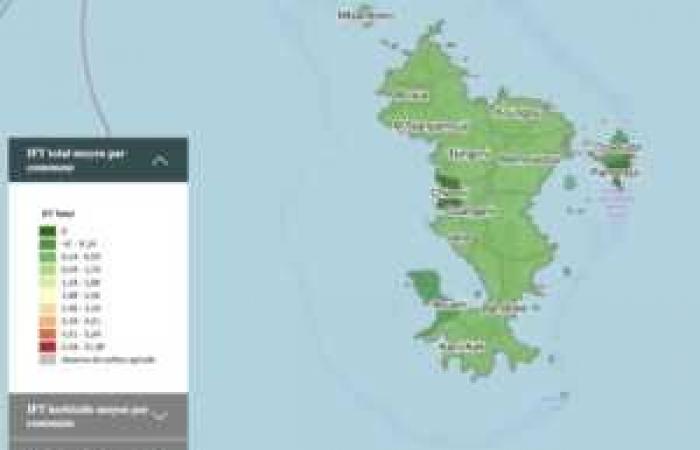
Intuitively easy to observe, and interactive, the Adonis map colors areas with low levels of pesticides dark green, and gradually evolving towards red for those that use them inconsiderately.
The municipal phytosanitary treatment frequency index (IFT) is an estimate of the level of pesticide use for each French municipality on the basis of the municipality's crop rotation (crop rotation), the type of practice (conventional or organic ) and regional reference IFTs derived from statistical or local data. The map comes from several cross-referenced data in mainland France, Solagro specifies that for the overseas departments, the work of its engineers made it possible to integrate the data from the different territories.
In mainland France, the North, the South-West and the South-East are the most densely exposed to phytosanitary treatment, unlike the central massif, Brittany and the East of France.
Overseas, the cultivation of sugar cane in Reunion and Guadeloupe is subject to high herbicide treatment, representing alone 53% of all pesticide treatments: “The use of herbicides is particularly high over a large part of the coastal areas of Reunion Island. The molecules used for weed control and their metabolites contaminate the environment (water) and authorizations for use are gradually withdrawn (like S-metolachlor, the use of which has been banned since April 2024).” The already highly subsidized sugarcane sector must also “continue the implementation of alternative practices to chemical weeding” to reduce the overall pressure of pesticides.
In Mayotte, under the green, Dimethoate
But we of course think of chlordecone in force for 20 years to protect the banana plantations of Martinique and Guadeloupe from the banana weevil, from 1972 to 1993 in the Antilles. “During these twenty years of use, this insecticide has caused pollution of soil, fresh water and the marine environment.” Farmers have been exposed to these practices themselves, with inherent health problems. Since then, the Sustainable Banana Plan has made it possible to develop treatments. “These improvements are visible in Guadeloupe with a drop of more than 50% in IFT since 2012 (from 6.74 to 3.2), unlike Martinique where the total IFT for bananas has remained high, around 7.3 on average since 2012. Which explains the strong coloring of the maps of the two departments. “Despite notable progress since the beginning of the 2000s, bananas remain one of the most processed crops in the overseas departments and regions, with only 4% of organic banana plantations in France in 2022.”
This is hardly the case in Mayotte where it is noted that “the dominant agroforestry and food-producing agricultural systems of Mayotte and Guyana allow these two departments to record reduced use of pesticides. »
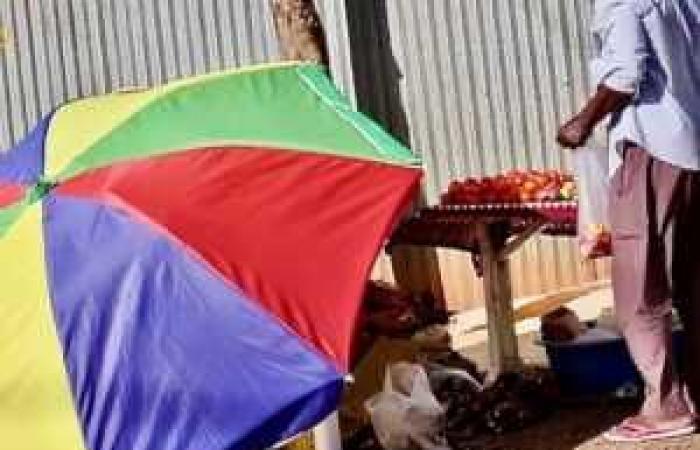
In our department, the use of pesticides such as Dimethoate, particularly in informal agriculture, prompts the Food Department to carry out regular checks with seizures of goods, particularly tomatoes whose doses exceed the legal rates. This was again the case last June, when the treatment with Dimethoate was increased, an insecticide banned since February 2016 by the European Commission, following the decision of the national food safety agency, environment and work (ANSES) judging this molecule as “presenting unacceptable risks for animals and humans”, noted the DAAF. But the areas affected have no comparison with the banana and cane sugar crops of other overseas departments.
Still in Mayotte, farmers were supported by the Ecophyto plan, which has now evolved into the “Ecophyto 2030 Strategy”. It is broken down into five areas: Accelerate the search for alternatives to prepare for the reduction in the number of authorized active substances; accelerate the deployment of agroecological solutions on all farms; better understand and reduce the risks to health and the environment from the use of plant protection products; research, innovation and training; and Territorialization, governance and evaluation.
By measuring the footprint of pesticides, these maps and tools allow the implementation of effective reduction policies, to encourage the agricultural transition towards more sustainable cultivation methods.
Anne Perzo-Lafond