The 2023 recommendations on polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are the first to be developed by four scientific societies, the European Societies of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) and Endocrinology (ESE) and the American Societies of Medicine reproductive (ASRM) and endocrinology. They had become necessary compared to those of 2018, endorsed solely by the ESHRE, to take into account progress in the diagnostic approach and the attention paid to screening and management of comorbidities.
A precise diagnostic algorithm
The clinical diagnostic criteria have not changed compared to those of 2018, or even compared to those of Rotterdam 2003, but their definition has been refined. The diagnosis is always based on the presence of two of these three elements: dysovulation, clinical and/or biological hyperandrogenism, presence of polycystic ovaries.
Cycle disorders are defined by a spacing of less than 21 days or more than 35 days, or the presence of less than eight cycles per year, or primary amenorrhea at the age of 15 years.
Hyperandrogenism clinical is characterized by the presence of clinical hirsutism, quantified by the Ferriman and Gallwey score; the existence of alopecia or acne can be taken into account, but little is known about their positive diagnostic predictive value. Biological hyperandrogenism is assessed by calculating free testosterone, based on the measurement of total testosterone and sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG). These assays should be carried out if possible by mass spectrometry, or by immunoassays with extraction and chromatography. The dosage of delta-4-androstenedione and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (SDHEA) is of little use as a second-line treatment, if testosterone is normal.
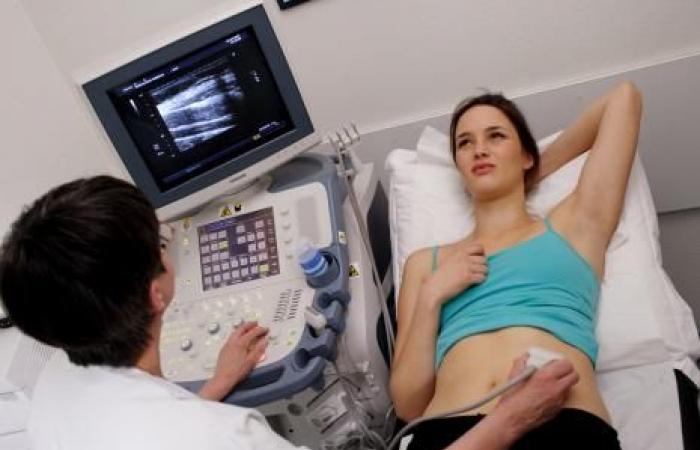
Ultrasound for the diagnosis of polycystic ovaries is done by endovaginal route. The diagnosis is made on the presence of at least 20 follicles with a diameter of less than 9 mm and/or a large ovarian volume (greater than 10 ml), without the presence of a cyst or dominant follicle. From now on, AMH measurement can be an alternative to ultrasound and the recommendations leave the choice between the two examinations for diagnosis.
Limit exams
Faced with irregular cycles and clinical hyperandrogenism, differential diagnoses must be eliminated, such as 21-hydroxylase block but also prolactin adenoma, Cushing’s syndrome, adrenal or ovarian tumors.
In the absence of clinical hyperandrogenism, we look for biological hyperandrogenism, which, associated with cycle disorders, allows the diagnosis to be made without further examination in the absence of other causes.
It is only in the absence of one of these two criteria – hyperandrogenism or cycle disorders – or in the presence of other gynecological symptoms that ultrasound is indicated.
“These new criteria make it possible to reduce the number of unnecessary endovaginal ultrasounds, particularly in adolescents, where the ultrasound should not be performed within eight years following the onset of menarche, due to the frequency of cysts. follicular, recalls Professor Anne Bachelot (La Pitie Salpêtrière, AP-HP). As we cannot rely on the AMH in adolescents either, we must remain on clinical criteria such as cycle disorders and hirsutism, to avoid both overdiagnosis without neglecting PCOS. »
Spotting complications
Women with PCOS are at risk of developing gestational diabetes or type 2 diabetes, so screening should be systematically performed at the time of diagnosis, regardless of body mass index, for oral hyperglycemia caused by 75 mg. It will be repeated every one to three years, depending on risk factors. Same recommendation for the lipid profile: to be done at diagnosis then every one to three years.
Blood pressure should be measured annually, and OSA should be identified systematically, for example using the Berlin questionnaire. Finally, depressive and anxious traits are common but underdiagnosed and insufficiently treated.
“The recommendations primarily emphasize lifestyle modification, particularly in terms of diet and physical activity,” underlines Professor Bachelot.
A global approach
Pharmacologically, spironolactone has recently received an indication in hirsutism. The prescription of cyproterone acetate is strictly regulated and reserved for severe hirsutism, at the lowest possible dose, after informing the patient and an MRI ensuring the absence of meningioma, and for a maximum duration of five years. , with, beyond that, MRI monitoring every two years.
Metformin, somewhat forgotten, is once again put forward for improving the metabolic parameters of these overweight or obese patients, whether or not they are diabetic, but it is still off-label in France. It improves other endocrinological symptoms a little, but less well than hormonal treatments.
Inositols, intracellular mediators of insulin action and capable of modifying hormonal responsiveness, are very fashionable, but the evidence for their effectiveness is limited and inconclusive. These food supplements are well tolerated, but very expensive and do not meet the same regulatory status in terms of dose and quality as medications.
Bariatric surgery has shown its effectiveness, not only on the metabolic level but also on the restoration of ovulatory function, and PCOS is recognized as a comorbidity allowing its indication.
Amenorrhea puts you at risk of endometrial cancer due to endometrial hyperplasia; It is therefore necessary to ensure at least three to four cycles per year, through the prescription of sequential progestins.
Interview with Professor Anne Bachelot (Paris)