THE ESSENTIAL
- Ethyl acetate extract is found in the leaves of Cajanus cajan, also called “pigeon pea”, which is a species of perennial plant in the Fabaceae family.
- The latter made it possible to reduce the severity of psoriasis and return the thickness of the epidermis of skin lesions to normal in sick mice.
- The mechanism involves activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and a subsequent reduction in the production of various inflammatory chemokines and cytokines.
Also known as pigeon pea, Cajanus cajan is a species of perennial plant in the Fabaceae family. It is present in Egypt, Africa and Asia. In ancient times, the juice extracted from its leaves was used to treat inflammation. “In southern China, it is used to relieve symptoms associated with various skin diseases,” according to researchers from the South China Botanical Garden (SCBG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. To determine the therapeutic effects and underlying mechanisms of Cajanus cajan leaves in the treatment of psoriasis, they conducted a study published in the journal Journal of Ethnopharmacology.
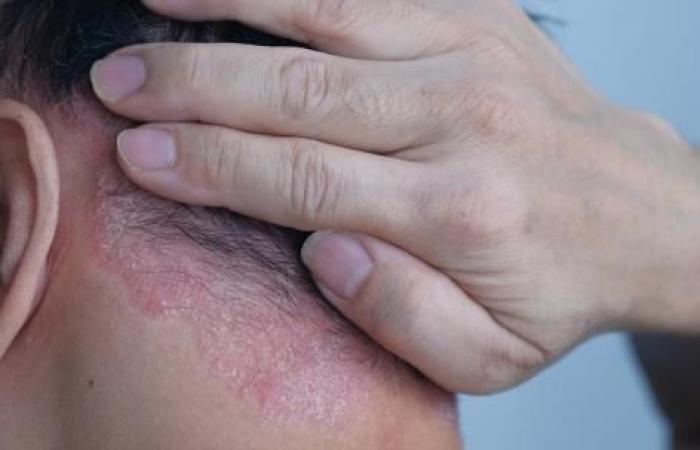
Psoriasis: ethyl acetate extract improves skin condition
As part of the work, the team extracted active components enriched in stilbenes, such as cajaninstilbene (12.32%), longistyline A (4.54%) and longistyline C (2.43%), from ethyl acetate (EtOAc) extract of Cajanus cajan leaves. Then, she administered the ethyl acetate extract once a day for 10 days to mice suffering from psoriasis induced by imiquimod, a substance that modifies the immune response. Its effectiveness in the treatment of psoriasis was evaluated by pathological analysis including weight change, disease severity, epidermis thickness and coloring of skin lesions.
According to the results, ethyl acetate extract of Cajanus cajan leaves effectively alleviated psoriasis symptoms in rodents. More precisely, it reduced the severity of this chronic pathology and improved the condition of the skin. In addition, the thickness of the epidermis of the skin lesions returned to normal after the administration of this plant extract.
A decrease in pro-inflammatory cytokines
Through further analysis, scientists found a significant decrease in several chemokines (Ccl2, Ccl20, Cxc5 and others), pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as Il17a, Il19, Il22, Il23, etc.) and associated genes. to keratinocyte differentiation (such as Lce and Sprr family genes). They concluded that the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), “a potential therapeutic target”and cytochrome P450 family genes are activated by ethyl acetate extract.
Faced with these data, researchers believe that the ethyl acetate extract of Cajanus cajan leaves has significant potential as a therapeutic agent of plant origin to treat psoriasis, which manifests itself as inflammatory plaques, red topped with strips of white skin. These lesions peel and may be itchy, which can affect quality of life.