This Saturday, an episode of freezing rain is expected in the country. This is rain falling in subzero temperatures! How is this possible?
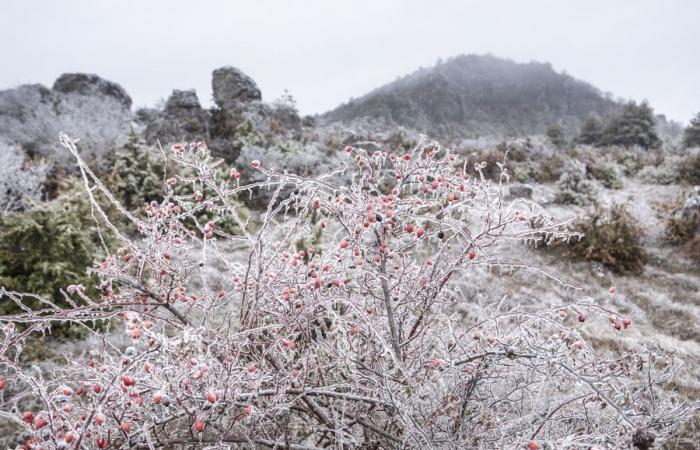
The famous “ice storm” of March 12, 2013 deposited ice sleeves reaching 24mm in the Perche. This is the most severe episode of freezing rain of the 21st century in France. – Illustration et archive Jérémie GAILLARD
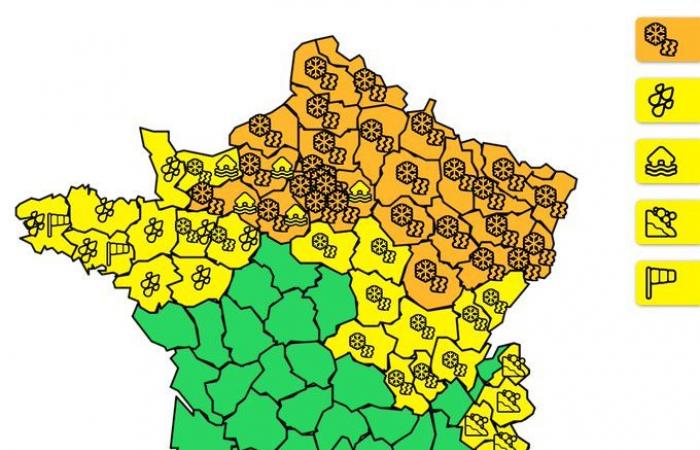
The Météo-France orange snow/ice vigilance concerns 30 departments during the evening of January 4, 2025
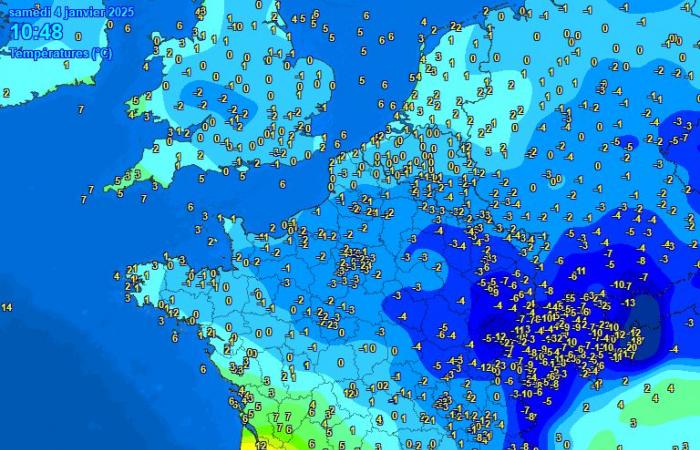
Today, we find a “warm front” type situation where a mass of mild air replaces a mass of cold air. This transition is clearly visible on the temperature maps.
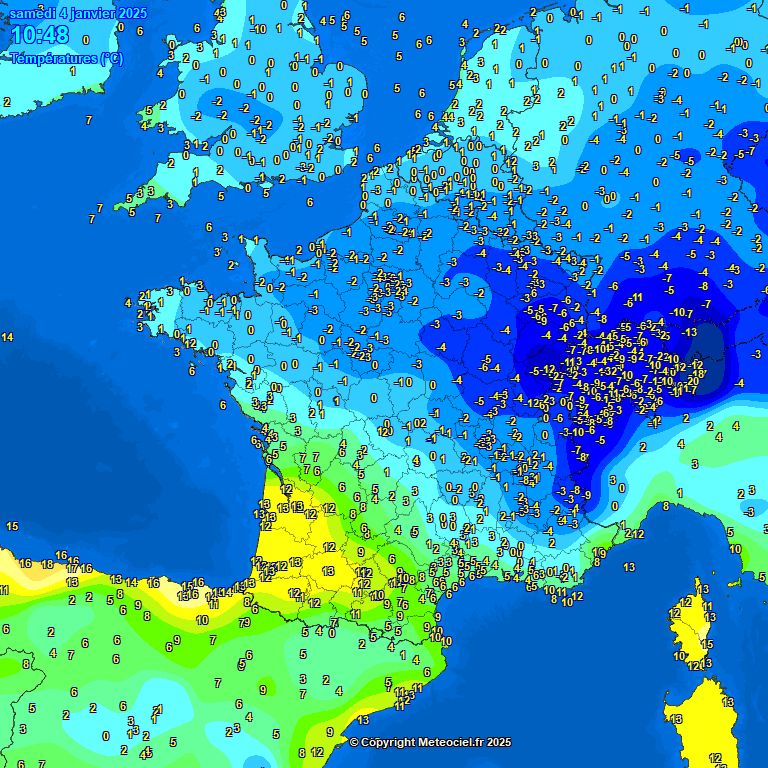
Evolution of temperatures during the day, the mild air coming from the South-West replaces the cold air present further to the North – Meteociel
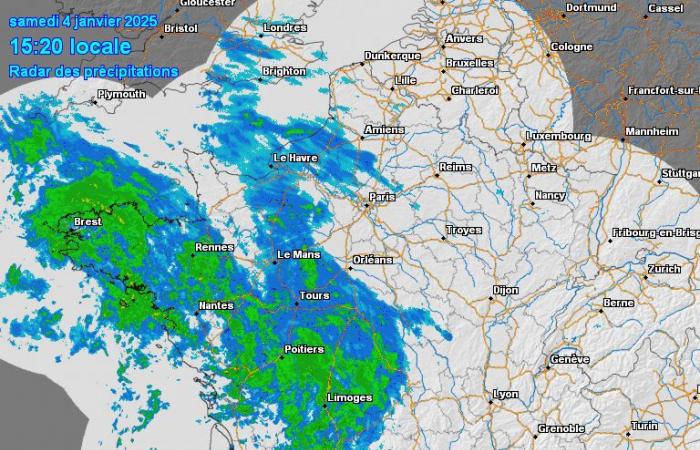
If you carefully observe the progress of the precipitation linked to this warm front, you will observe a phenomenon that could seem strange…
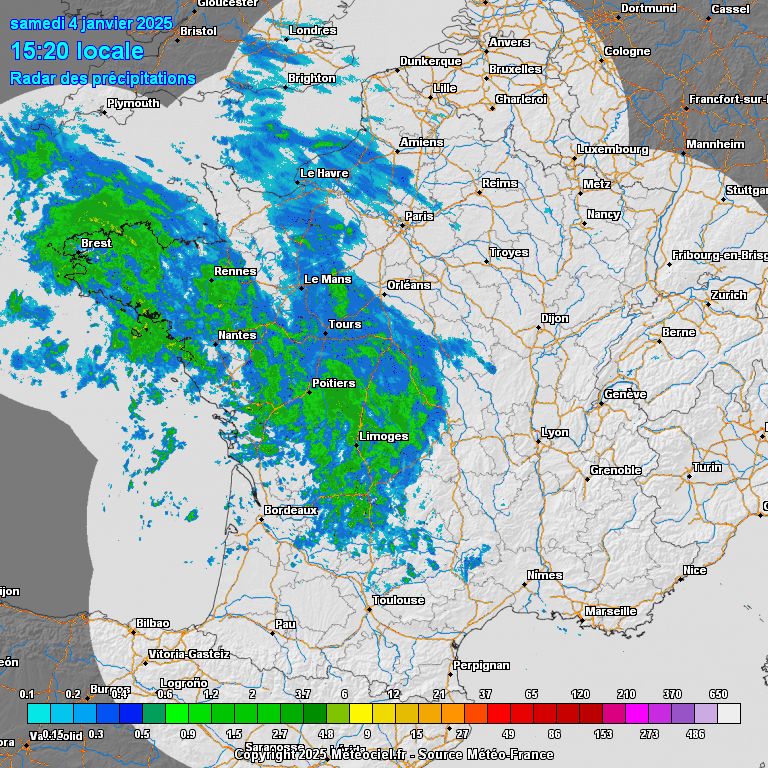
Radar imagery this Saturday January 4, 2025 – Meteociel
With an animation at the same speed (step of 30min, 10fps versus step of 1h, 5fps for the temperature animation), the rain seems to go much faster than the hot air rises. This is due to the nature of a warm front:
– Cold air is heavier, pressed to the ground and subject to significant friction (difficult to set in motion and therefore difficult to expel).
– Warm air is lighter and spreads faster at altitude, with stronger winds.
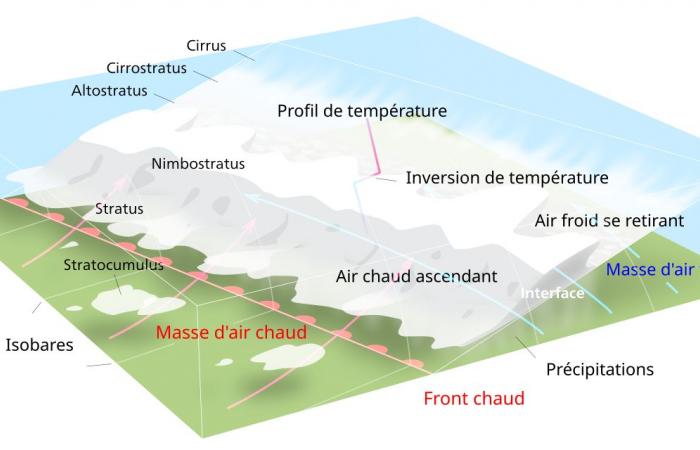
The precipitation which will form at the level of the mixture between the two air masses will therefore tend to follow the warm air at altitude, and to advance faster than the cold air withdraws at ground level…
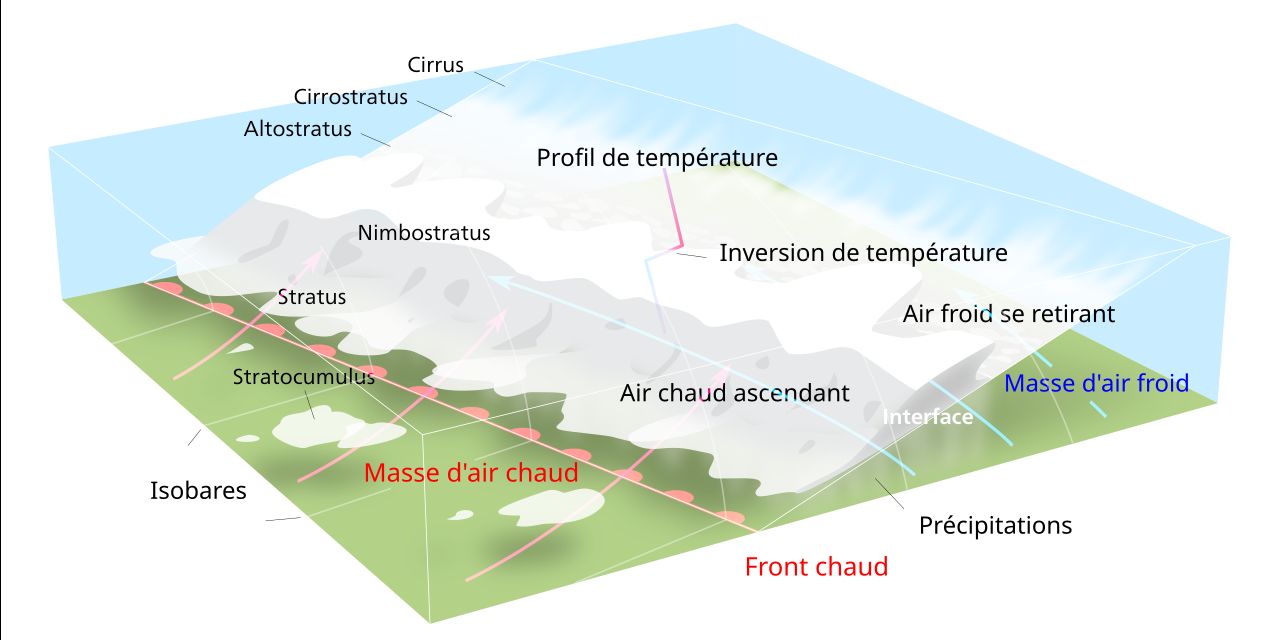
Representation of a warm front where warm air moves more quickly at altitude, and tends to cover the cold air pressed to the ground – Pierre cb / Wikipedia
In winter, the cold air located close to the ground may well be at negative temperatures, while the warm air already begins to reach higher altitudes. There is therefore the formation of a “sandwich” of temperatures with a hot layer located between two layers at negative temperatures. It is this phenomenon that interests us today.
-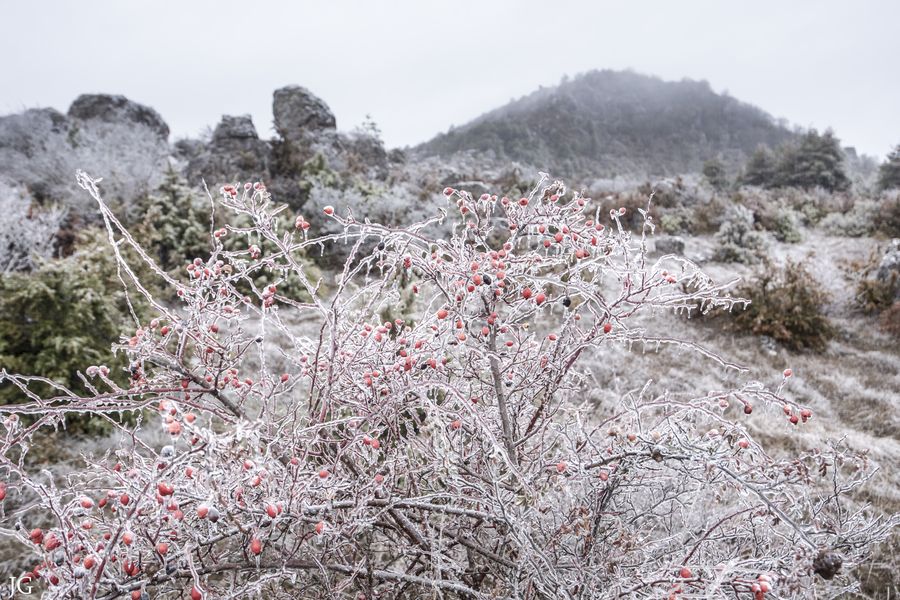
Freezing rain on rose hips observed in Caylar (Causse du Larzac) on December 10, 2017 – Illustration Jérémie GAILLARD
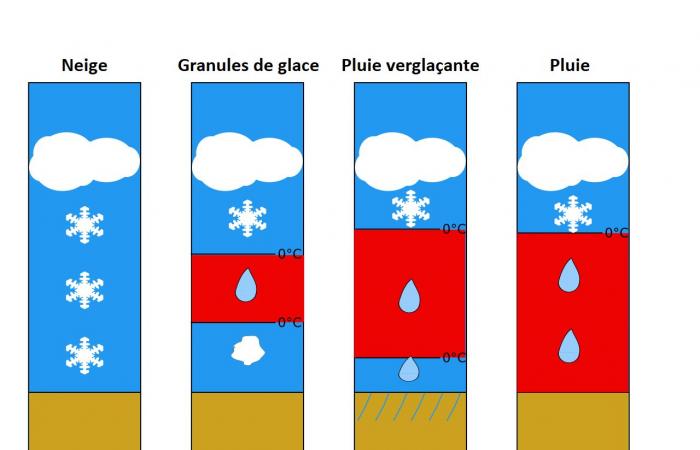
Indeed, while the first precipitation may occur as snow, the warm air will eventually melt the snow at altitude and change it to rain.
– If the layer of cold air close to the ground remains thick enough, the rain will refreeze and ice pellets will fall.
– If the layer is thin enough, the water will temporarily supercool. Rain will fall in a liquid state in negative temperatures! It will therefore freeze instantly on the frozen ground, producing ice… The famous freezing rain.

Diagram of the different precipitation found during the presence of a layer of mild air at altitude – Wikipedia
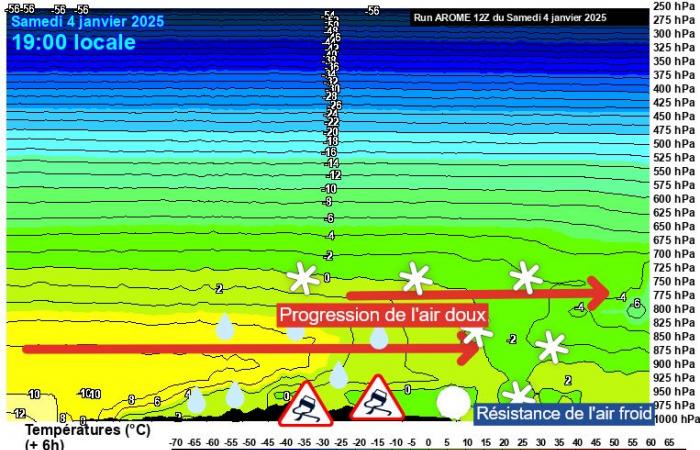
If we look at cross-sectional weather models today, it is possible to see this mass of warm air circulating aloft. On a section going from Pays de la Loire to Picardy, we can see that the profile is favorable to a staggering of the types of precipitation going from a short strip of snow, to ice granules then to freezing rain, for finally turn to classic rain at positive temperatures.
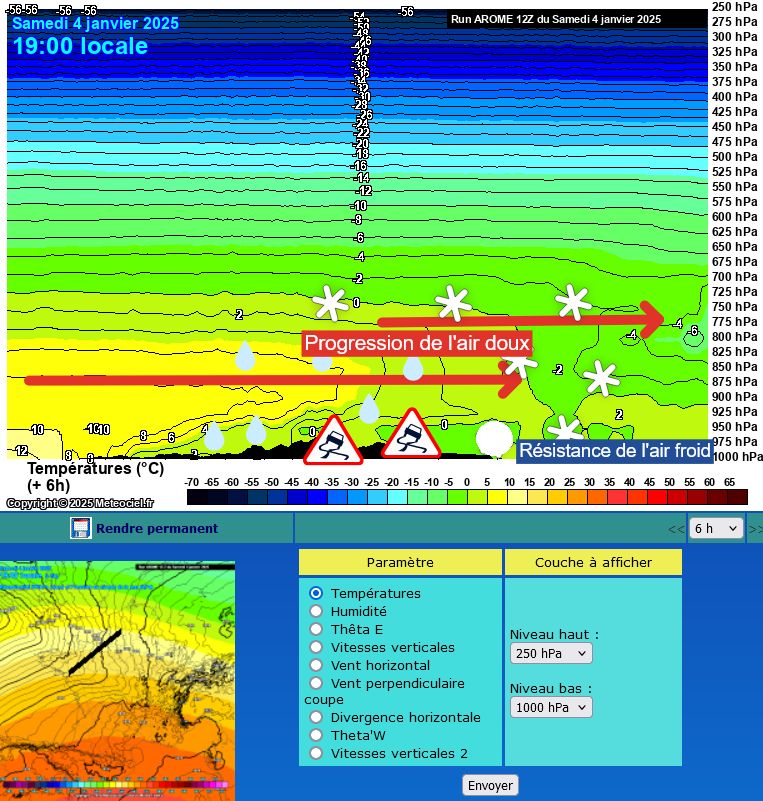
Cross-sectional modeling of the warm front on January 4, 2025 at 7 p.m. – Arome/Meteociel
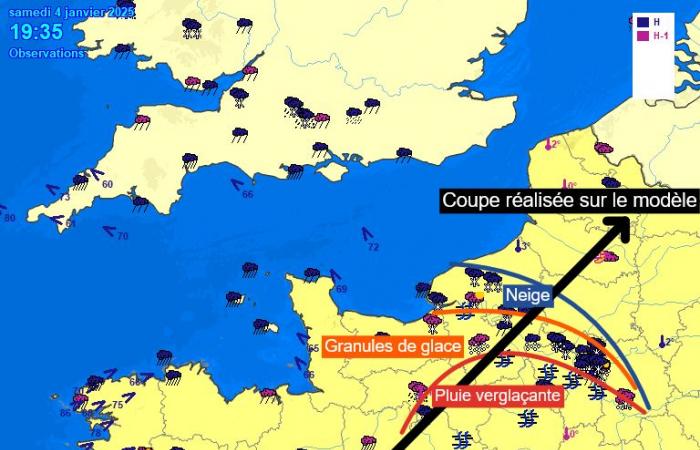
If we look at the observations against the cut made on the model at this time, the influence of the tongue of warm air aloft on the types of precipitation observed is evident.

Observations of sensitive weather on January 4, 2025 at 7:35 p.m. – Meteociel
Jérémie GAILLARD – Forecaster for MétéoCilles