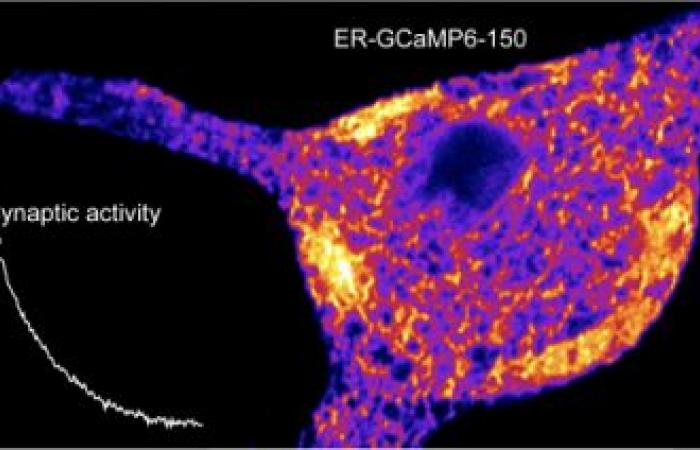
Mitochondria, intracellular organelles, play a major role in neuronal functions, by controlling 3 fundamental mechanisms essential to neurobiology and synaptic transmission:
- The production of ATP (Adenosine-TriPhosphate)
- Calcium homeostasis
- Cell death by apoptosis
Using cutting-edge optical technologies to study the bioenergetics of active synapses in combination with targeted manipulations of metabolism and genetics, the team will dissect the molecular mechanisms by which synaptic mitochondria control normal and pathological neuronal function. The aim of this work is:
- To better understand the neurophysiological role of mitochondria in synaptic metabolic integrity
- To consolidate knowledge on the link between mitochondrial dysfunctions and metabolic epilepsies
- To serve as a basis for future studies to improve the bioenergetics of mitochondria in neurological diseases of mitochondrial origin
Main publications
Ashrafi, G.*, de Juan-Sanz, J*, Farrell, R.J. and Ryan T.A. (2020). Molecular tuning of the axonal mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter ensures metabolic flexibility of neurotransmission. Neuron, 105(4):678-687.e5. * Co-first authors.
De la Rocha-Muñoz, A., Núñez, E., Gómez-López, S., López-Corcuera B., de Juan-Sanz J* and Aragón C (2020). The presynaptic glycine transporter GlyT2 is regulated by the Hedgehog pathway in vitro and in vivo. * Corresponding author. BioRxiv.doi:https://doi. org/10.1101/2020.07.28.224659.
De la Rocha-Muñoz A., Núñez, E., Arribas-González, E., López Corcuera,B., Aragón, C* and de Juan-Sanz J* (2019). E3 ubiquitin ligases LNX1 and LNX2 are major regulators of the presynaptic glycine transporter GlyT2. * Co-corresponding authors. Scientific Reports. Sci Rep 9, 14944
Koopmans F, van Nierop P, Andres-Alonso M, (…) Malenka R, Nicoll RA, Pulido C, de Juan-Sanz J, Sheng M, Südhof TC, (…) Thomas PD, Smit AB, Verhage M (2019) . SynGO: An Evidence-Based, Expert-Curated Knowledge Base for the Synapse. Neuron, 103(2):217-234
De Juan-Sanz, J., Holt, G. T., Schreiter, E. R., de Juan, F., Kim, D. S., & Ryan, T. A. (2017). Axonal endoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ content controls release probability in CNS nerve terminals. Neuron, 93(4), 867-881