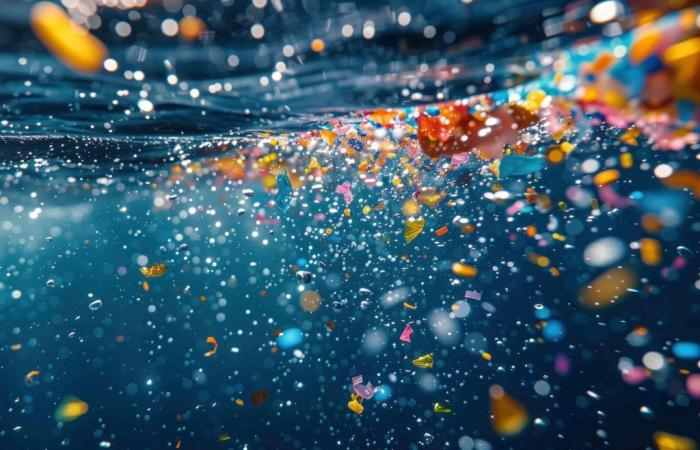
Microplastics are particles of plasticplastic which are smaller than five millimeters. They come from a variety of sources, including the degradation of larger plastic waste, personal care products, synthetic textiles, and industrial processes. Their ubiquity in the environment and ability to persist for centuries raise major concerns. As researchers begin to unravel the mysteries of their environmental impact, understanding how these particles affect human health is crucial.
Mechanisms of exposure to microplastics
Microplastics enter the human body mainly through ingestioningestion et inhalationinhalation. Food and beverages, particularly seafood, bottled water and processed products, are common sources of ingestion. Studies have found microplastics in human feces, confirming their passage through the digestive system. Inhalation of particles in theairairespecially in urban environments, is another route of exposure. Inhaled particles can be deposited in the respiratory tract and even reach the pulmonary alveolipulmonary alveoli.
Once in the body, microplastics can cross biological barriers, such as the intestinal wall, and potentially reach various organs. Small particles, especially those smaller than 1 micrometermicrometercan be absorbed more easily and distributed through the bloodstream. Preliminary research suggests that they may accumulate in organs such as the foiefoieTHE reinsreins and the brainbrainalthough the exact mechanisms and consequences of this accumulation remain to be clarified.
Effects of microplastics on human health
The effects of microplastics on human health are still largely unknown, but several pathways toxicitytoxicity are considered. The particles themselves can cause inflammationsinflammations and some oxidative stressoxidative stressbiological responses that can lead to cellular damage. Microplastics can also act as vectors for other toxic substances, such as metalsmetals heavy, persistent organic pollutants and agents pathogenspathogensthus increasing their harmful potential.
Some animal studies have shown that exposure to microplastics can cause harmful effects on the immune systemimmune systemthe reproductive system and the endocrine systemendocrine system. In humans, although data are still limited, there are indications that inhalation of microplastics could exacerbate respiratory diseases, such asasthmaasthmaand that their ingestion could have repercussions on digestive and metabolic health.
Furthermore, the presence of microplastics in food products could have indirect implications for public health, by affecting food quality and safety. Degraded plastics can release chemical additives, such as phthalatesphthalates and bisphenols, known for their effects endocrine disruptorsendocrine disruptorsand thus contribute to hormonal imbalances and fertility problems.
Microplastics represent an emerging threat to human health, although their precise effects still require extensive research. The mechanisms of exposure, through ingestion and inhalation, and the potential pathways of toxicity highlight lightlight the importance of understanding and controlling this invisible pollution. As scientists continue to explore this issue, it becomes imperative to take steps to reduce the production and use of plastics, while improving waste management methods to minimize their environmental and health impact.