This study, carried out by a team led by Syria Laperche of the French Blood Establishment (EFS), in collaboration with Public Health France, the CNR of Sexually Transmitted Infections and Inserm, sheds light on the evolution of syphilis among donors of blood, a distorted reflection of developments in the general population. The study focuses on syphilis screening data on 45,875,939 blood donations made between 2007 and 2022, the majority of which (39,180,092) were donations from regular donors. Syphilis is systematically looked for and remains a criterion for removing positive tests. Remember that until 2016 to ensure the security of donations with regard to the HIV Human immunodeficiency virus. In English: HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus). Isolated in 1983 at the Pasteur Institute in Paris; recent discovery (2008) rewarded by the Nobel Prize in Medicine awarded to Luc Montagnier and Françoise Barré-Sinoussi. sexual relations between men were a criterion for exclusion from blood donation. This exclusion was considered discriminatory given the tests that have long been used to reliably rule out HIV-positive donations. In 2017 the Complidon study counted only 0.73% (95% CI: [0,63-0,83]) of male donors had not declared having had sex between men in the last 12 months during the predonation interview.
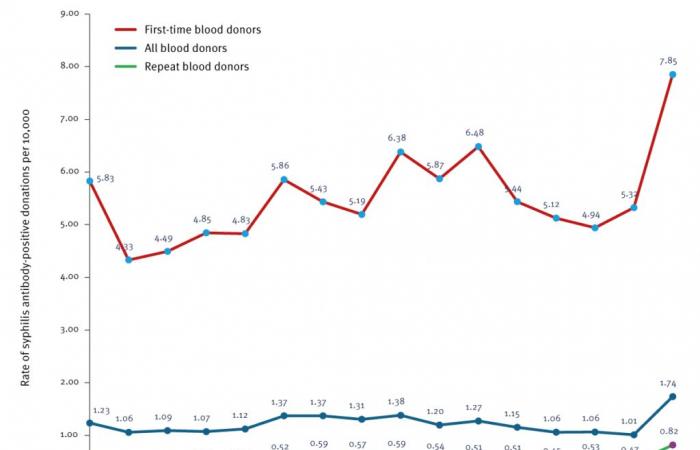
The results based on the serological test show a significant increase in syphilis in 2022: the positivity rate which had remained relatively stable between 2007 and 2021, with an average of 1.18 cases per 10,000 donations, reached 1.74 cases per 10,000 donations in 2022. Rates are much higher for first donations than for regular donors. The increase between 2020 and 2022 is observed in some (from 4.94 per 10,000 in 2020 to 7.85 in 2022) as in others (from 0.54 to 0.82). Over the entire period studied, the prevalence Number of people affected by a given infection or other disease in a given population. was 2.2 times higher among men than among women, it is increasing. This disparity widened in 2022, with a prevalence 4.1 times higher among male donors. And among these, the proportion of men who have sex with men (MSM) among syphilis-positive donors has logically increased, from 16.7% in 2007 to 64.9% in 2022. Incidence measured among repeat donors shows a different trend from the prevalence among all donors: it increases from 4.66 per 100,000 person-years in 2012-2014 and 5.61 in 2014-2016, to 4.67 in 2017–2019 and 3.96 in 2020–2022. However, it must be remembered that this population of regular donors is particularly selected.
Source: Eurosurveillance.
In the general population, trends published in October 2024 by Public Health France based on information from patients seen in CEGIDD Free information, screening and diagnosis center (CeGIDD) for human immunodeficiency virus infections, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections. These centers have replaced the free anonymous screening centers (CDAG) since January 1, 2016. on the one hand, cases identified in the SNDS on the other hand, are consistent with the increase observed in blood donations, with an increase in the SNDS of 20% in 2023, even more marked among women (27% ) than in men. However, the gap in prevalence between men and women remains very wide: 16 per 100,000 among men and 2 per 100,000 among women.
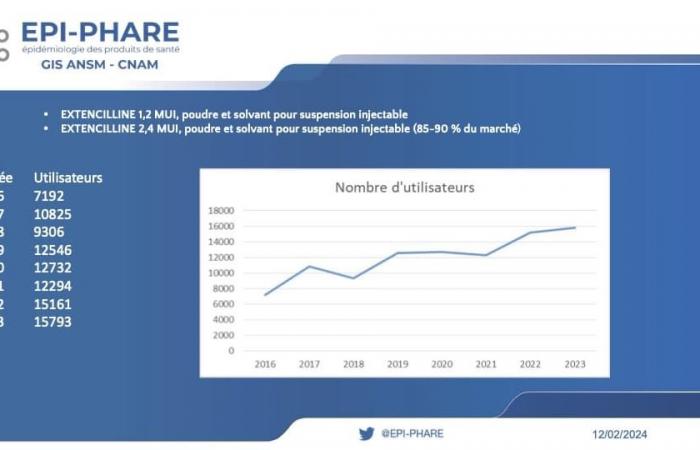
Extencillin delivery volumes – the main indication of which is syphilis – can be seen as a complementary indicator, even if supply disruptions can alter its validity. Contacted on this subject, Dominique MARTIN, national medical officer of the CNAM, also reports a regular growth of 4% in patients on extencillin between 2022 and 2023. This growth is 22.6% between 2021 and 2022.
Mahmoud Zureik, director of GIS EPI-PHARE, shares the following data, based on the number of extencillin deliveries reimbursed by health insurance.
The increase in syphilis is being observed in other European countries and the United States, making surveillance particularly necessary generally and in blood donations.
The failure of a strategy based on NTT to distinguish recent from old syphilis
Although there has been no transfusion-transmitted syphilis for years, the WHO still recommends testing blood donations for syphilis. Furthermore, a European directive (2002/98/EC) only requires a postponement of donation for one year after the infection has been cured. In this context and with the increase in cases of syphilis in the population, it would be particularly interesting and useful to identify recent syphilis, in order to allow people who have had long-standing syphilis to donate blood. It is with this aim that the authors evaluated a screening strategy including NTT as a possible option to identify recent syphilitic infection.
Syphilis-positive donations collected in 2022, according to presumed date of infection based on post-donation interview and cardiolipid antibody titer, France, 2007-2022 (n = 429)
History of syphilis NTT Titlea : ≥ 8 NTT Titlea : 1-4 NTTa : 0 Negative Total n % ≤ 1 an 1 3 3 0 7 1.6 >1 an – 3 ans 29 18 44 0 91 21.2 > 3 years 0 23 92 1 116 27 Not aware of an infection 27 13 33 1 74 17.2 No information 22 51 68 0 141 32.9 Total 79 (18.4%) 108 (25.2%) 240 (55.9%) 2 (0.5%) 429NTT: non-treponemal test.
a Launch Diagnostics ASI RPR Card Test (Arlington Scientific) on the Gold Standard Diagnostics AIX 1000 RPR Automated Analyzer.
Source : https://www.eurosurveillance.org/content/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2024.29.32.2400036
Among the 474 HIV-positive donors in 2022, 429 underwent additional examinations with an NTT. Based on these results, 79 donors (18%) were classified as having been infected in the previous year. The history of syphilis in post-donation interviews was only available for 30 out of 79. But only 30% of donors with syphilis acquired within 3 years had an NTT titer > 8 compatible with active infection. What’s more, with an algorithm based on the use of TT and NTT, detection by an ultrasensitive test for treponemal antibodies, automated by chemiluminescence technique (CLIA) but negative in NTT can correspond either to early syphilis, to syphilis treated, latent syphilis of unknown duration or even a false positive as seen in pregnant women in particular. The authors conclude that they have not succeeded in identifying a biological diagnostic strategy capable of distinguishing old infections from recent infections.
Thus, given the difficulty in certifying healing; a permanent exclusion of donors confirmed positive for syphilis remains applied in France. It will disproportionately affect MSM Man having sex with other men. due to increased exposure to syphilis.
Resurgence of syphilis in the United States
Syphilis is experiencing an alarming resurgence in the United States, reaching its highest level since 1950 in 2022, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Public health experts increasingly recognize that testing and treatment alone will not be enough to stem this epidemic.
In 2022, 207,255 cases of syphilis were reported in the United States, an increase of 17.3% year-over-year. Of these cases, 3,755 were cases of congenital syphilis, linked to 282 stillbirths and infant deaths. The rate of congenital syphilis reached 102.5 cases per 100,000 live births, the highest since 1991. The most affected populations are American Indians and Alaska Natives (67 cases per 100,000), followed by the black population (44.4 per 100,000).
To address this problem in its complexity, a federal task force named “National Syphilis and Congenital Syphilis Syndemic (NSCSS) Federal Task Force” was created in August 2023. The term “syndemic” was chosen to emphasize the interaction between syphilis and other health conditions like HIV, hepatitis C, and substance use including fentanyl and methamphetamines. The pandemic of COVID-19 Coronavirus disease, sometimes referred to as coronavirus disease, is an illness caused by a coronavirus (CoV). The term may refer to the following diseases: severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) caused by the SARS-CoV virus, Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) caused by the MERS-CoV virus, coronavirus disease 2019 ( Covid-19) caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. has also played a role in exacerbating pre-existing health disparities and straining an already fragile public health infrastructure.