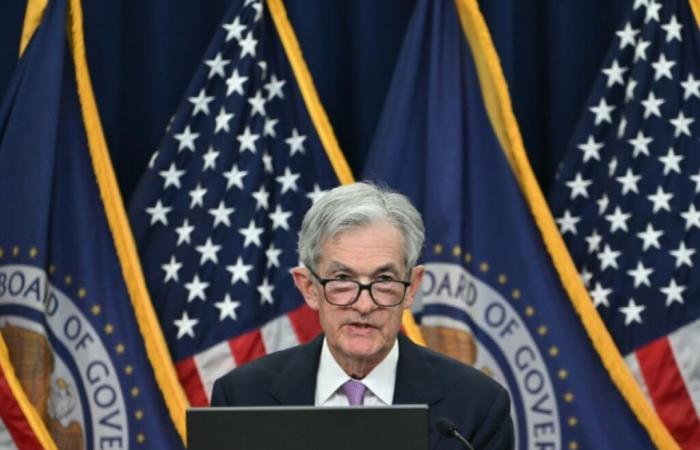
Fed President Jerome Powell during a press conference on November 7, 2024 in Washington (AFP / ANDREW CABALLERO-REYNOLDS)
The American Central Bank, the Fed, lowered its rates by a quarter of a percentage point on Thursday, the day after the re-election of Donald Trump which could herald tumultuous days for the monetary policy institution.
This new cut places rates in the range of 4.50 to 4.75%. It comes after that of half a point in September – the first since March 2020.
The Fed meeting began on Wednesday, a day late than the usual schedule, due to the presidential election won by Republican Donald Trump.
“In the short term, the elections will have no effect on our decisions,” said Fed Chairman Jerome Powell during his press conference.
The American Central Bank, the Fed, lowered its rates by a quarter of a percentage point on Thursday as expected, welcoming the drop in inflation and the easing of the job market, the day after the re-election of Donald Trump ( AFP / Mandel NGAN)
“We don't know what the timing and type of reforms will be and therefore we don't know what the effects on the economy might be. We don't guess, we don't speculate, we don't assume,” he said. he continued.
Jerome Powell, however, refused to comment on a possible weakening of the independence of the Fed under this new Trump administration.
The Republican billionaire was in fact accustomed to interference in monetary policy during his first mandate, and recently felt that he should have “his say” in the decisions taken by the institution.
– “Non” –
Jerome Powell also assured that he would not resign before the end of his mandate if the White House asked him to do so. When asked during the press conference, he simply replied “no”.
Before specifying that the law “does not allow” the dismissal of the governors of the powerful institution.
These comments come as Donald Trump signaled in July, after sowing doubt, that he would let Jerome Powell complete his term as Fed chairman, which ends in May 2026. His term as governor, which is separate, ends in January 2028.
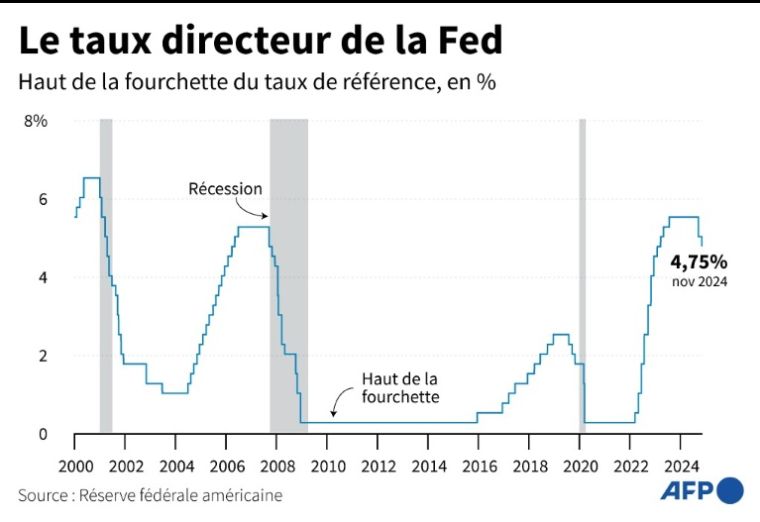
Evolution of the Fed's key rate since 2000 (AFP / Patricio ARANA)
Jerome Powell was chosen in 2012 by former Democratic President Barack Obama to join the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve, then Donald Trump himself promoted him to president in 2018.
On the economic front, the president of the Fed praised the solidity of the American economy.
The Fed's Monetary Policy Committee, the FOMC, reported in its press release “labor market conditions (which) are easing overall”, after a period of labor shortage which had contributed to push prices up.
– “Progress” of inflation –
As for inflation, which the Fed brought down by raising rates to slow demand, it “has made progress in its return to the 2% objective (…) but remains high”.
It fell in September to its lowest level since February 2021, to 2.1% over one year, according to the PCE index, favored by the Fed.
To slow it down, the central bank raised its rates to their highest since the early 2000s, and kept them at that level for more than a year, until September.
The increases in customs duties promised by Donald Trump could, however, cause inflation to rebound.

Donald Trump during election night in West Palm Beach, November 6, 2024 in Florida (AFP / Jim WATSON)
Washington recently released a series of indicators showing solid economic activity, but moving away from post-Covid euphoria.
GDP (gross domestic product) growth in the third quarter disappointed, but remains almost twice as strong as that of the euro zone, at 2.8% at an annualized rate.
Job creation was very weak in October, due to hurricanes and strikes, particularly at Boeing.
The decision to cut rates was made unanimously by the FOMC, which did not update its economic forecast this time, with the next update expected at the next meeting in December.
Across the Atlantic, the Bank of England (BoE), which also met on Thursday, lowered its key rate by a quarter of a point, for the second time this year, to 4.75%.