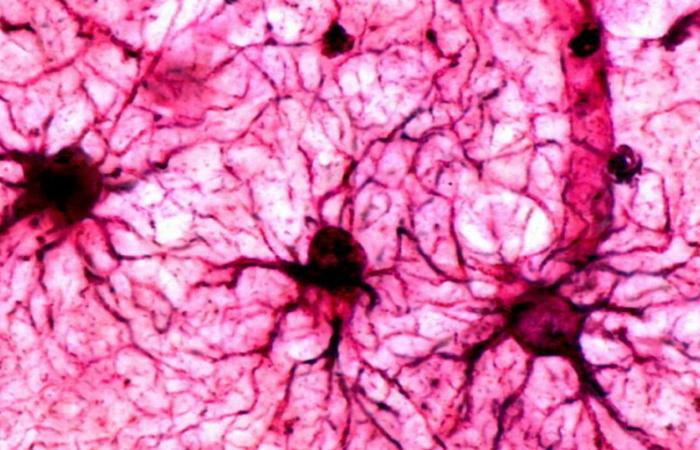
UA new understanding of our memories is emerging thanks to the study of astrocytes, star-shaped cells present in the brain. Long considered as nourishing supports, these cells keep – like neurons – the physical and chemical traces of past events.
American researchers have just shown that the inactivation of certain astrocytes blocks the formation of memories associated with fear.
In the laboratory, neuroscientists first conditioned rodents to freeze when subjected to specific situations that were frightening for them. The astrocytes activated at the time of this learning were identified.
Then in a neutral situation, the researchers reactivated these cells, which caused the fear reflex in the conditioned rodents.
A new perspective
Conversely, their study shows that if these astrocytes are inactivated during fear conditioning, the mice are unable to fix this frightening memory in their memory. This discovery offers a new perspective on the understanding and management of post-traumatic stress disorders. (Nature)
Health